from the book by E.N. Orlova and E.R. Varchenko "UAZ Cars" Maintenance and repair
Cooling system.
Cooling system(fig. 25) liquid, closed, with forced circulation.
Rice. 25 Engine cooling system diagram
1 - heater radiator
2 - heater tap
3 - cylinder head
4 - holes of the water distribution pipe
5 - gasket
6 - water distribution pipe
7 - thermostat
8 - outlet branch pipe
9 - filler neck
10 - blinds
11 - cork
12 - minimum mark
13 - tank
14 - pump of the cooling system
15 - impeller
16 - pulley
17 - fan
18 - radiator
19 - radiator drain valve
20 - inlet pipe
21 - the block of cylinders
22 - drain valve of the cylinder block
Low-freezing liquid antifreeze A-40 is used as a coolant. At an ambient temperature below minus 40 C, antifreeze liquid A-65 is used. The use of water is allowed.
For normal engine operation, the coolant temperature must be maintained within 80 ... 90 C. This is achieved using an automatically operating thermostat and blinds controlled by the driver.
To control the temperature of the coolant in the instrument panel there is an electric pointer, the sensor of which is screwed into the cavity of the bracket of the water pump. In addition, overheating of the coolant is signaled by a control lamp with a red filter installed on the instrument panel and connected by an electric wire to a sensor screwed into the upper radiator tank. The control lamp lights up when the coolant reaches a temperature of 92 ... 98 C. When the control lamp comes on, open the radiator shutters.
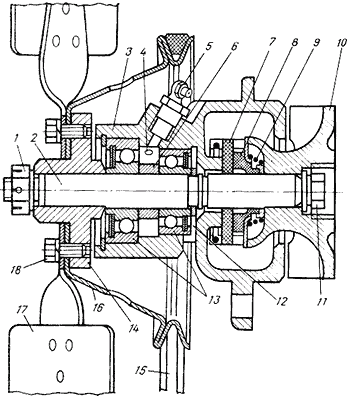 Rice. 26 Engine cooling pump
Rice. 26 Engine cooling pump
1 - nut
2 - shaft
3 - pump casing
4 - control hole for the lubricant outlet
5 - grease nipple
6 - spacer sleeve
7 - sealing washer
8 - rubber cuff
9 - spring
10 - impeller
11 - the impeller mounting bolt
12 - control hole for liquid outlet
13 - bearings
14 - fan shaft hub
15 - belt
16 - pulley
17 - ventilator
18 - bolt
Engine cooling system UMZ-42164-80
Rice. 12 Cooling system diagram.
1 - interior heater radiator; 2 - radiator valve; 3 - water jacket; 4 - block head; 5 - gasket; 6 - inter-cylinder channels for the passage of the coolant; 7 - thermostat; 8 - thermostat housing; 9 - branch pipe of the thermostat body (large circle of circulation); 10 - steam outlet pipe; 11 - expansion tank; 12 - filler neck plug; 13 - mark "min"; 14 - coolant temperature sensor; 15 - branch pipe for removing liquid from the expansion tank; 16 - cooling system pump; 17 - water pump impeller; 18 - cooling system fan; 19 - two-way radiator of the cooling system; 20 - water pump branch pipe; 21 - radiator drain plug
The first control loop consists of an automatically acting thermostat that regulates the amount of fluid entering the radiator. Depending on the position of the thermostat valve, the ratio of fluid flows passed for cooling to the radiator and returned back to the engine changes. The second control loop is realized by controlling the operation of the electromagnetic clutch for the fan drive, due to which the amount of air passing through the radiator grilles changes. The switching on and off of the electromagnetic clutch is carried out by the relay according to the commands received from the controller.
During operation, the coolant must be poured and topped up into the cooling system through the expansion tank 11 by opening the filler cap 12. The liquid vapors and evolved air formed in the system are discharged from the radiator and thermostat housing through the steam pipe 10. In order to avoid cavitation during pump operation 16, its suction cavity is connected to the expansion tank by means of a branch pipe 15.
For normal engine operation, the temperature of the coolant at the outlet from the head must be maintained within the range of plus 81 ° - 89 ° C.
A short-term operation of the engine at a coolant temperature of 105 ° C is permissible. Such a mode can occur in the hot season when the car is moving with full load on prolonged ascents or in urban driving conditions with frequent accelerations and stops.
Maintaining the operating temperature of the coolant is carried out using a single-valve thermostat with solid filler T-118-01 installed in the housing.
When the engine warms up, when the coolant temperature is below 80 ° C, a small circle of coolant circulation operates. The thermostat valve 7 is closed.
The coolant is pumped into the cooling jacket 5 of the cylinder block 6 by a water pump, from where, through the holes in the upper plate of the block and the lower plane of the cylinder head, the liquid enters the cooling jacket of the head 3, then into the thermostat housing 14 and into the supply branch of the interior heating radiator 1. Depending from the position of the valve of the interior heating valve 2, the coolant either through the heating radiator or bypassing it enters the connecting pipe and then to the inlet of the water pump. The two-way radiator 19 of the cooling system is disconnected from the main flow of the coolant. The circuit of fluid circulation implemented in this way makes it possible to increase the efficiency of heating the passenger compartment when the fluid moves in a small circle (this situation can be maintained for a long time at low negative ambient temperatures).
When the liquid temperature rises above 80 ° C, the thermostat valve opens and the coolant circulates in a large circle through the two-way radiator.
For proper operation, the cooling system must be completely filled with liquid. When the engine warms up, the volume of liquid increases, its excess is pushed out due to the increase in pressure from the closed circulation volume into the expansion tank. When the temperature of the liquid drops (after the engine stops working), the liquid from the expansion tank is returned to the closed volume under the action of the resulting vacuum.
The coolant level in the expansion tank should be 3-4 cm above the "min" mark. Due to the fact that the coolant has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, and its level in the expansion tank changes significantly depending on the temperature, the level should be checked at a temperature in the cooling system of plus 15 ° C.
The tightness of the cooling system allows the engine to operate at a coolant temperature exceeding + 100 ° C. When the temperature rises above the permissible level (plus 105 ° C), the temperature alarm is triggered (a red lamp on the instrument panel). When the temperature warning lamp comes on, the engine must be stopped and the cause of overheating eliminated.
The reasons for overheating can be: insufficient amount of coolant in the cooling system, weak tension of the coolant pump drive belt.
A warning. Do not open the expansion tank cap when the coolant in the cooling system is hot and under pressure, otherwise serious burns may occur.
The coolant is poisonous, so avoid getting it into the mouth or on the skin.
The coolant pump is shown in fig. 13.
Thermostat housing is die-cast from aluminum alloy. Together with the housing cover, it distributes the coolant to the outside of the engine cooling system, depending on the position of the thermostat valve (Fig. 14)

Rice. 13. Coolant pump:
1 - hub; 10 - pulley; 3 - body; 4 - retainer; 5 - bearing; 6 - fitting for draining the coolant from the heating system; 7 - cover; 8 - impeller; 9 - oil seal; 10 - control hole.

Rice. 14. Scheme of the thermostat: a - the position of the thermostat valve and the direction of the coolant flow when the engine is warming up; b - after warming up.
1 - thermostat housing; 2 - fitting of the interior heating radiator (small circle of coolant circulation); 3 - thermostat; 4 - steam outlet fitting; 5 - branch pipe of the thermostat housing; 6 - gasket.
Electromagnetic clutch for shutdown of the fan is shown in Fig. 15.
The switching on and off of the clutch is carried out by the relay according to the commands received from the controller of the engine management system.
After starting the engine at a low coolant temperature, the rotation of the pulley to the driven disk and the associated fan hub 2 with the bearing is not transmitted, because the end of the pulley and the driven disc are separated by a gap A. The required gap is provided by adjusting the position of the three tabs of the driven disc stop. In the extreme right position, the driven disc is held by three leaf springs.
After the engine warms up and the coolant reaches a temperature of + 89 ° C, the controller sends a command to the relay to turn on the electromagnetic clutch. The relay closes the contacts and supplies current through the connector to the coil winding. The resulting magnetic flux is closed through the driven disk and attracts it to the end of the pulley, overcoming the resistance of three leaf springs. The fan hub 2, like the fan itself, begins to rotate at the same time as the pulley.
When the temperature drops below 81 ° C, the controller turns off the relay, which breaks the power circuit of the coil winding. Under the action of three leaf springs, the driven disk moves away from the end of the pulley by the amount of clearance A. The fan hub together with the fan stops rotating. When the coolant temperature rises above 89 ° C, the process is repeated.
The maintenance of the clutch consists in checking the clearance A, and, if necessary, adjusting it using a flat feeler gauge 0.4 mm thick by bending the three stops of the driven disc.
The coupling must be periodically cleaned of dust and dirt. Additional lubrication of the coupling during operation is not required.
Almost all car enthusiasts know that a car has an engine cooling system. UAZ Loaf or 452 is equipped with a simple design power unit, and therefore the rest of the systems have simple design features.
The purpose of the cooling system
The UAZ Loaf engine cooling system is designed to cool the engine during operation. So, the cooling elements remove the generated heat from the cylinder block and the head with the help of coolant and cool it in the radiator.
During operation, the power unit of the car heats up to exorbitant temperatures and if there is no cooling, then the engine parts will simply overheat and deform. Although, such situations also occur in the presence of a coolant system, in the case when it is not in working order or one of important elements out of order.
The operating temperature of the engine on the UAZ Loaf is 80-100 degrees Celsius. It is in this interval that the thermostat opens to a large cooling circle.
Since on this car an electric fan is not provided, but there is a forced cooling system, then additional cooling of the radiator is constantly on.
The power unit can overheat if one of the cooling elements is out of order. First, there will be an easy stage, in which the motor will simply boil. But, there can be serious consequences, such as deflection and deformation of the cylinder head. At this stage, the situation can be corrected by ordinary grinding the surface of the block head.
![]()
In the middle stage, engine elements may deform. These include valve train... Subsequently, the block head will need overhaul, and this will come out in a considerable penny to the owner vehicle.
The hard stage is when it collapses piston group from strong exposure to heat. But, and this is not the worst thing that can happen, because if the coolant gets into the cylinders of the car, then the engine will overtake a water hammer, in which the overhaul does not always save.
Coolant system diagram
The scheme of the UAZ engine cooling system is quite simple, it is of a closed type with forced circulation of the coolant. The "cooler" circulates in a circle from the radiator, passing the water pump and thermostat into the cooling jacket, and then returns.
Consider the cooling scheme of the power unit on UAZs, and in particular on the engine marked 452:
![]()
Cooling system element
The main elements of the cooling system of the power unit of the UAZ Bukhanka 452 engine are well-known parts: a radiator, a fan, a water pump, a thermostat, pipes, a water jacket and a temperature sensor. Also, a heater is part of the design.
So, let's consider what the main elements of engine cooling are, their structure and operation, as well as repair and revision.
Radiator and fan
UAZ vehicles can be equipped with 3-row copper or aluminum radiators, which provide maximum cooling of the liquid. Since the operation of the elements is quite long, the cooling process of the power unit is not always the same as it should be.
In this case, this is due to clogging of the channels inside the element. Often, ordinary cleaning does not help, and increased wear makes cracks in the pipes, which the owners actively solder, not wanting to buy new parts. The main purpose of the radiator is to cool the fluid that circulates from the engine using the wind flow.
The fan of the cooling system on the Loaf is forced, fixed on the pulley and runs constantly until crankshaft spinning. Many car enthusiasts are upgrading this system and install electric fans, which are often turned on by the driver himself according to the temperature readings on the dashboard.
![]()
Water pump
The pump for the UAZ is a mechanical drive. The main purpose of the element is to continuously circulate coolant through the system. So, the water pump provides a flow of liquid to the radiator for cooling and vice versa. A malfunction of this element can lead to the loss of "cooling" and overheating of the engine.
Thermostat
The main structural element is a thermostat. It circulates fluid and serves as a switch between the small and large circle in the system. To warm up the vehicle, the element is kept closed. When it reaches 80 degrees Celsius, it starts to open, thereby circulating fluid through the radiator.
The main malfunction can be considered a jamming of the element, which can lead to overheating of the motor, since, as practice shows, the thermostat wedges on a small circle, and accordingly there will be no additional cooling and fluid flow through the radiator.
Nozzles and water jacket
Nozzles are a means of transporting fluid through the system from the engine and its elements to the radiator and vice versa. Failure of these elements leads to the loss of "cooling", which, in turn, lowers the coolant level in the system, and this is a direct path to overheating.
Water jacket - design features of the block head and cylinder block. It is through these holes that the coolant flows, which takes away heat for cooling. With a long service life, especially in water, corrosion can form inside the walls, which will lead to leaks and loss of fluid.
![]()
temperature sensor
The temperature sensor on the Loaf is not the same as most motorists are used to seeing. This is an old-style element that does not include an electric fan, since a forced system is installed here, but simply outputs to dashboard temperature indicators.
Output
As you can see, the diagram of the UAZ Bukhanka (452) engine cooling system is quite simple. It can be easily repaired, and broken parts can be replaced without much difficulty. This unit consists of components - radiator, fan, water pump, thermostat, pipes, water jacket and temperature sensor.
The coolant sensor is fundamentally different from modern ones, since it does not turn on the fan, but simply shows the temperature of the "cooling".
The malfunctions of the cooling system pump (hereinafter referred to as the pump) are:
Destruction of the pump bearing assembly. It manifests itself in the form of abnormal noise. When rocking the pump pulley by hand, you will feel a play in the bearings
Destruction of the oil seal or the pump sealing washer. This failure is usually the result of excessive play in the bearings. It manifests itself in the form of coolant leaks in the area of the pump flange.
Deformation of the body (cracks, warpage) of the pump due to overheating or mechanical shock.
In all of the above cases, immediate repair or replacement of the pump is required. Since its complete failure will lead to overheating of the engine, which is fraught with warpage of the cylinder block or cylinder head.
Faults in the engine thermostat are partial or complete jamming of the thermostat valve in one of the positions. Jamming of the thermostat valve in the upper position (open a large circle of coolant circulation) is not dangerous. This only affects the increase in engine warm-up time. In winter conditions, this can result in the engine being unable to reach operating temperature.
Much more dangerous is the jamming of the thermostat in the lower (closed) position, when the coolant circulates only in a small circle. This leads to overheating of the engine.
Indirectly, a thermostat stuck in the lower position can be calculated by the heating of the upper radiator pipe. If the temperature of the upper pipe is noticeably lower than the engine temperature, then with a high degree of probability it can be argued that the thermostat valve "stuck" in the closed position.
A complete picture of the state of the thermostat can be obtained by heating it to 90 ° in a container with water. When the water temperature reaches ~ 70 °, the thermostat valve should open. If this does not happen, then the thermostat is faulty and must be replaced.
When replacing the pump, it is also advisable to replace the coolant.
It must be remembered that when replacing the coolant, it is important not to mix fluids with different bases. Namely, ethylene glycol-based fluids and propylene glycol-based fluids. Again:
IT IS NOT ALLOWED TO MIX COOL BASED ON ETHYLENE GLYCOL AND PROPYLENE GLYCOL! The alkalinity of this mixed solution is such that it corrodes any metal in a very short period of time.
Typically, ethylene glycol coolants are colored green, yellow or blue in practice. Based on propylene glycol - red. But this is just my observation, no matter what, you need to carefully study the composition of the coolant, which the manufacturer indicated on the label.
Regarding the general terms of replacing the coolant, then for ethylene glycol fluids, this is 60,000 km. mileage or 3 years, whichever comes first. Replacement of ethylene glycol coolants is caused by the fact that an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol itself is a very aggressive liquid to metals and therefore a complex of neutralizing additives (inhibitors) is introduced into its composition. Over time, these additives are destroyed and no longer protect the parts of the cooling system, and the coolant must be changed.
Propylene glycol-based fluids are less aggressive, so the replacement period for such coolants is every 5 years. Or 100,000 km of run.
Last but not least, all alcohol-based coolants are extremely toxic !! Observe precautions - do not inhale vapors, do not allow coolant to get on open skin and under no circumstances allow coolant to enter the body! 35cm3 is a lethal dose for humans!
Required tool:
Socket set - 10, 12, 13, 17, ratchet and wrench
Combination wrench set - 10, 12, 13
Screwdriwer set
Hose dia. 10mm and a length of at least 40cm
Capacity for drained coolant - at least 15 liters.
Long nose pliers
A. Replacing the thermostat:
1. Drain the coolant from the engine and radiator (if you only plan to change the thermostat, then all the coolant does not need to be drained, it is enough to drain 4-5 liters). There are 2 taps for this - one on the right on the block, the other on the left on the radiator. If the machine is equipped with standard pre-heater, then instead of the tap on the block, drain the coolant through the tap in the heater boiler.
Attention! The stove tap must be open and the radiator cap removed!
Putting one end of the hose on the tap, and lowering the container on the other, pull the pull of the tap flag. If there is no draft, then by hand we turn the faucet flag clockwise.
Faucet on the block:
Faucet on the radiator:

2. After waiting until the coolant is completely drained (or the required volume is drained), use a screwdriver to unscrew the clamps of the upper radiator pipe. Then, with a key or a 12 head, unscrew the 2 bolts securing the thermostat housing cover.
Remove the cover together with the upper pipe. We take out the thermostat. If you cannot remove it with your hand, then grabbing it with long-nose pliers, swinging it from side to side, tear it out.
3.Installation of the thermostat. The thermostat must be installed and oriented in such a way into the housing so that a small (~ 2mm) hole in which a rivet hangs is located in the highest place relative to the thermostat valve.
This is due to the fact that this hole is intended for air outlet during refueling of the coolant system, and since air bubbles always accumulate in the highest place, then the hole should be located at the highest.
Approximate orientation of the thermostat:

When installing the thermostat cover back, you need to clean the seat from traces of the old gasket, otherwise the cooling system may leak.
4. Fill with coolant. We warm up the engine to operating temperature, then, after waiting for the engine to cool down to 40-50 °, we check the coolant level. Top up if necessary.
B. Replacing the pump:
1. We carry out step 1 from the section "Replacing the thermostat".
2. Remove the alternator belt. If the machine is equipped with a power steering, then first remove the power steering pump belt and only then the generator belt.
Attention! Do not leave the belts hanging on the crankshaft pulley, they can get coolant or oil and cause the belts to break.
3. Remove the side shields of the radiator. We unscrew the 2 bolts securing the upper rods of the radiator mounting. We take the traction to the side.
4. Remove the fan. To do this, unscrew 4 bolts, while holding the fan from turning by hand by the blade.
Then, tilting the radiator as far forward as possible, we drag the fan between the casing and the pump pulley. We remove the pump pulley, which was held by the same bolts.
5. Remove the fan shroud. It is fastened with 4 M6 bolts and a radiator faucet pull.
6. Unscrew the clamps securing the remaining pipes of the cooling system.
We remove the pipes from the pump, thermostat housing and radiator.
7. Remove the stove hose clamp and dismantle the hose from the pump connection
8. Next, I recommend removing the radiator. Although, it is possible with some difficulty to remove the pump without dismantling the radiator. But I don't recommend it. First, remove the hoses from the oil cooler. Then we wrap the wire of the emergency temperature sensor. Afterwards, unscrew the screws securing the cable for the shutter rotation mechanism with a screwdriver.
The radiator itself is mounted on 2 supports from below. Use long-nose pliers to unpin the nuts and turn them around with a head of 17. Remove the radiator by pulling it up.
After removing the radiator, turn it over with the filler neck down and drain the rest of the coolant from the radiator. Approximately 0.5 liters. It is also advisable to rinse the removed radiator.
From the inside - 10% soda solution, from the outside - a jet of water under low pressure and a very soft brush.
9. Remove the pump. If the pump is of a new type (the same as on the 421 engine), then it is fastened with 6 nuts. It is more convenient to turn them off with the head by 13. The generator bar is attached to one of the studs. Having unscrewed 6 nuts, we pull the pump off the studs. Together with the pump, its back cover is also removed.
As a result, you should get the following:

If, when unscrewing the pump nuts, one (or several) of the studs broke off, then you can do 2 ways: use a hairpin driver or a welding machine.
Stud runner:

Or put a nut on the hairpin and weld it:

10. Carefully remove traces of the old gasket on the block. To do this, you can use a drill with a brushed brush on it. Particular attention is in the area of hairpins, where it is most difficult to clean out qualitatively from the old gasket. It is better to put a new gasket on the sealant. It's safer this way.

11. We put the pump. After the pump back cover gasket has been installed, you can mount the pump itself back. It is placed in the same way as it is removed. 12. We carry out the assembly in the reverse order.
We carry out point 4 of the section "Replacing the thermostat"
When refueling the cooling system, the liquid must be poured into the radiator with a thin stream. This is necessary to prevent airing of the system.
The UMZ 417 engine was intended for installation in soviet cars off-road Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant, such as UAZ 469 and UAZ 452 "Loaf".
Peculiarities. The UMZ 417 motor has replaced. The engine got a new cylinder head similar to the cylinder head of the GAZ-24 (). The compression ratio increased from 6.7 to 7.0. The changes also affected the gas distribution mechanism - a different camshaft and new intake valves were installed (the cap diameter was increased to 47 mm). A cylinder head with round windows for a manifold, on early engines a manifold for a single-chamber carburetor. Two-chamber carburetor on engines with an index of 4178.
The problems of the motor have long been known - poor quality of parts and assembly, problematic cooling system (the motor is prone to overheating), oil leaks from everywhere, even through the block.
The resource of the UMZ-417 engine is about 150 thousand km.
The engine has a number of modifications (see below).
Engine characteristics UMZ 417 UAZ 469, 452 Loaf
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Configuration | L |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Volume, l | 2,445 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 92,0 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 92,0 |
| Compression ratio | 7,0 |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 (1-inlet; 1-outlet) |
| Gas distribution mechanism | OHV |
| The order of the cylinders | 1-2-4-3 |
| Engine rated power / at engine speed | 66.9 kW - (92 hp) / 4000 rpm |
| Maximum torque / at engine speed | 177 N m / 2200-2500 rpm |
| Supply system | Carburetor K-151V (G) |
| Recommended minimum octane number of gasoline | 76 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 0 |
| Weight, kg | 166 |
Design
Four-stroke four-cylinder gasoline carburetor with a contact ignition distributor, with in-line cylinders and pistons rotating one common crankshaft, with the bottom arrangement of one camshaft... The engine has a closed-type forced circulation liquid cooling system. Lubrication system - under pressure and spray.
Aluminum cylinder block with cast iron sleeves... In UMZ-417, the liners are planted through rubber rings, in contrast to the ZMZ-402, which fit through copper gaskets. Unfortunately the rubber rings reduce the strength of the 417 motor block. The block has no stiffeners. Only on later engines did 3-4 ribs appear. On the UMZ-417 unit there is a mount for an oil filter from a VAZ-2101.
If we continue to talk about the similarities and differences between the UMZ-417 and ZMZ-402 engines, then we can say that the crankshaft, camshaft, connecting rods, pistons, rings, pushers and rods are the same. The liners are different due to the different fit. The flywheel of the 417th is larger in diameter and heavier, respectively, the bell is also larger in size. At ZMZ, the packing is put into the groove in the block and the crankshaft cover, while at UMP it is screwed and crimped with stamped steel plates, which ultimately has a bad effect on the tightness of the structure.
At UMP 417, the coolant is taken and supplied to the cylinder head, as a result of uneven cooling of the engine. The ZMZ 402 pump is more reliable than the 417th, it has an oil seal, not a fiber. But this only applies to the old-style pump! Now on the new pumps for the 417th motor, an oil seal is used.
It is important to mention that the exhaust manifold on the UMP 417 has a 4-1 design, which crushes the engine at medium and high speeds.
Modifications
1. UMP 417.10 - designed for installation on UAZ-3151 vehicles (76 gasoline, 92 hp).
2. UMP 4175.10 - has an increased compression ratio of 8.2 for 92 gasoline. Power 98 HP Used on Gazelle cars.
3. UMP 4178.10 - used a manifold for a two-chamber carburetor.
4. UMP 4178.10-10 - installed cylinder head with increased exhaust valves up to 39mm. Complete with crankshaft oil seal instead of packing. The pump is fixed to the block. designed for UAZ vehicles.
Service
Oil change in engine UMP 417.
Oil change interval - 10 thousand km. The oil volume of a dry engine with an oiled cooler is 5.8 liters. When replacing, 0.5 to 1 liter of oil remains in the lubrication system and the radiator. Oil filter from VAZ 2101. Oil recommended by the manufacturer - M-8-B SAE 15W-20, M-6z / 12G SAE 20W-30, M-5z / 10g1, M-4z / 6B1 SAE 15W-30.
Adjustment of valves It is necessary to adjust the gaps every 15 thousand km.


