How the engine's work is related to the choice of driving style
First, the main specifications engines installed on Logan:
Let's consider in more detail power and torque:
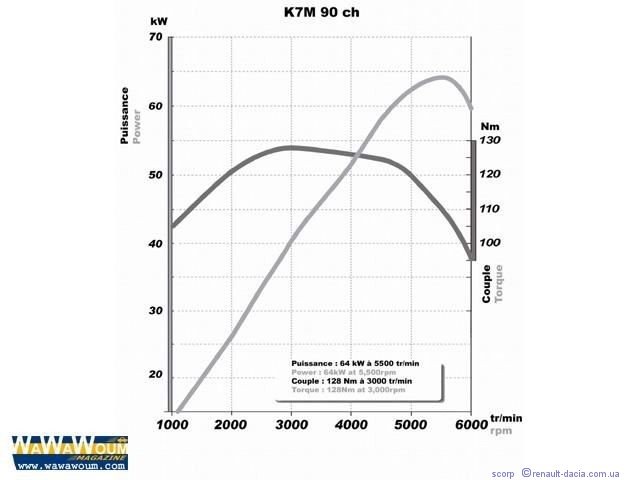

The most interesting characteristic is torque, which shows the traction capabilities of the engine. Power however, it directly affects only the maximum speed.
Maximum power and torque are developed only at certain engine speeds, which can be seen on the graphs and on the car's tachometer while driving.
For example, for my 1.4L engine, the optimal zone is from 3000 to 5000 rpm. If these revs are maintained with timely gear changes, then the car behaves most responsively, accelerating with the maximum possible force, which has a beneficial effect on safety, since it allows you to make, for example, overtaking as quickly as possible.
"Unscrew" the engine, i.e. it makes sense to move at less than 3000 rpm only when driving quietly, without maneuvering, to save fuel.
"Twist" over 5500 rpm. does not make sense at all, tk. maximum speed it is achieved in the highest gear at 5500, and in other gears, after 5000 rpm. engine thrust decreases sharply.
Another important characteristic is " elasticity"engine. It is usually described as the ability of the engine to accelerate the car at high speeds. For example, from 60 km / h to 100 km / h.
It is calculated as the ratio between the rpm of the maximum power and the rpm of the maximum torque.
For engines from the first table, the elasticity is equal to: 1.83; 1.83; 1.53 respectively.
Apparently, although 16 valve engine and is more powerful and stronger than its younger counterparts, but it has less elasticity, which should be taken into account when overtaking on the track.
Good luck on the road! And don't forget about reason.
Renault Logan cars are equipped with K7M and K7J gasoline engines. These engines are identical in design and differ only in displacement.
The K7M engine of Renault Logan cars has a working volume of 1.6 liters, and the K7J engine has a volume of 1.4 liters. The increase in displacement is obtained due to the larger radius of the crankshaft crank / greater piston stroke.
Brief technical characteristics of the Renault Logan K7M engine
Type - Gasoline, 4-stroke, 4-cylinder, in-line, 8-valve
Location - Front, transverse
Engine Power System - Multiport Fuel Injection
Cylinder diameter and piston stroke, mm - 79.5x80.5
Working volume, cm3 - 1598
Compression ratio - 9.5
Rated power, kW (hp) - 64 (87) at a crankshaft rotation speed of 5500 rpm
Maximum torque, Nm - 128 at a crankshaft rotation speed of 3000 rpm
Fuel - Unleaded gasoline with an octane rating of at least 91
Ignition system - Electronic, part of the engine management system
Fig. 1. K7M Renault Logan engine with auxiliary units
1 - air conditioner compressor; 2 - accessory drive belt; 3 - generator; 4 - power steering pump; 5 - oil level indicator (oil dipstick); 6 - cylinder head cover; 7 - ignition coil; 8 - spark plugs; 9 - cylinder head; 10 - thermostat housing; 11 - exhaust manifold; 12 - coolant pump pipe; 13 - oxygen concentration sensor; 14 - oil pressure sensor; 15 - technological plug; 16 - flywheel; 17 - cylinder block; 18 - oil pan; 19 - oil filter
K7M car engine Renault Logan petrol, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, overhead camshaft... The order of operation of the cylinders: 1-3-4-2, counting from the flywheel.
The power supply system of the Renault Logan engine is distributed fuel injection (Euro-2 toxicity standards). K7M engine with gearbox and clutch form power unit- a single unit fixed in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal bearings.

Fig. 2. Renault Logan engine (Powertrain)
1 - gearbox; 2 - crankshaft position sensor; 3 - inlet pipeline; 4 - sensor of absolute air pressure in the intake manifold; 5 - intake air temperature sensor; 6 - throttle assembly; 7 - regulator idle move; 8 - oil filler cap; 9 - fuel rail; 10 - oil level indicator (oil dipstick); 11 - cylinder head; 12 - cylinder block; 13 - drive belt auxiliary units; 14 - oil pan; 15 - knock sensor; 16 - support bracket of the inlet pipeline; 17 - starter; 18 - vehicle speed sensor
The right support is attached to the bracket on the upper cover of the timing belt (timing), and the left and rear support to the gearbox housing.
The cylinder block of the Renault Logan engine is cast from cast iron, the cylinders are bored directly in the block. The nominal cylinder diameter is 79.5 mm. In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five crankshaft main bearing supports with removable covers, which are attached to the block with special bolts.
The holes in the cylinder block of the Renault Logan K7M engine for bearings are machined with the covers installed, therefore the covers are not interchangeable and are marked on the outer surface for distinguishing (covers are counted from the flywheel side).
On the end surfaces of the middle support, sockets are made for thrust half rings that prevent axial movement of the crankshaft.
The liners of the main and connecting rod bearings of the Renault Logan engine crankshaft are steel, thin-walled with an anti-friction coating applied to the working surfaces.
Crankshaft with five main journals and four connecting rod journals. The shaft is equipped with four counterweights 1 (p. 64), cast together with it. To supply oil from the main journals to the connecting rods, channels 2 are used, the outlet openings of which are closed with plugs.
At the front end (toe) of the crankshaft of the K7M engine are installed: an oil pump drive sprocket, a timing gear (timing) drive gear pulley and an auxiliary drive pulley.
In the hole toothed pulley there is a protrusion that fits into the groove on the toe of the crankshaft and fixes the pulley from turning. Similarly, it is fixed on the shaft and the accessory drive pulley. A flywheel 3 is attached to the crankshaft flange with seven bolts.

Fig. 3. Flywheel of the K7M engine of Renault Logan cars
1 - wreath for the crankshaft position sensor; 2 - a crown for starting the engine
A flywheel is installed on the Renault Logan engine, which is cast from cast iron and has a pressed-on steel ring for starting the engine with a starter. In addition, a ring gear for the crankshaft position sensor is provided on the flywheel.
Connecting rods - steel, I-section, processed together with caps. The covers are attached to the connecting rods with special bolts and nuts.
Piston pin - steel, tubular section. The pin pressed into the upper connecting rod head rotates freely in the piston bosses.
The piston of the Renault Logan engine (K7M) is made of an aluminum alloy. The piston skirt has a complex shape: in the longitudinal section it is barrel-shaped, in the transverse section it is oval.
In the upper part of the piston, there are three grooves for piston rings 4. Top two piston rings- compression, and the bottom - oil scraper.

Fig. 4. Renault Logan cylinder head
1 - cylinder head fastening screw; 2 - camshaft support; 3 - valve spring; 4 - spring plate; 5 - crackers; 6 - lock nut; 7 - an adjusting screw; 8 - bracket; 9 - a camshaft pulley; 10 - valve rocker; 11 - bolt of fastening of an axis of rocker arms of valves; 12 - the axis of the rocker arms of the valves; 13 - thrust flange of the camshaft
The Renault Logan engine has an aluminum alloy cylinder head that is common to all four cylinders. It is centered on the block with two bushings and secured with ten screws.
A non-shrinkable metal gasket is installed between the block and the head. There are five camshaft bearings (bearings) on the top of the cylinder head.
The supports are made one-piece, and the camshaft is inserted into them from the timing drive side. Camshaft driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft.
In the extreme bearing journal of the camshaft (from the flywheel side) of the Renault Logan engine, a groove is made, which includes a thrust flange that prevents axial movement of the shaft.
The thrust flange is attached to the cylinder head with two screws. From above to the camshaft supports, the valve rocker shaft is attached with five bolts. The rocker arms are held against displacement along the axis by two brackets, which are fastened with the rocker arm axis bolts.
Screws are screwed into the rocker arms, which are used to adjust the thermal clearances in the valve drive 5. The adjusting screws are secured against loosening with locknuts.
The seats and valve guides of Renault Logan engines are pressed into the cylinder head. On top of the valve guides, the valve stem seals are put on.
Steel valves, arranged in two rows, inclined to the plane passing through the cylinder axes. In front (in the direction of the vehicle) there is a row of exhaust valves, and in the back there is a row of intake valves. The inlet valve disc is larger than the outlet valve.
The valve is opened by a rocker, one end of which rests on the camshaft cam, and the other, through an adjusting screw, on the end of the valve stem.
The valve of the K7M Renault Logan engine closes under the action of a spring. With its lower end, it rests on a washer, and with its upper end, on a plate, which is held by two crackers.
The folded crackers on the outside have the shape of a truncated cone, and from the inside they are equipped with persistent collars that go into the groove on the valve stem.
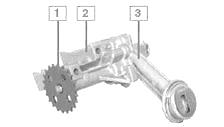
Fig. 5. Renault Logan engine oil pump
1 - driven sprocket of the drive; 2 - pump casing; 3 - pump casing cover with oil receiver
Renault Logan engine lubrication - combined. The main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft and the bearings of the camshaft are lubricated under pressure. Other engine components are spray lubricated.
The pressure in the lubrication system is generated by a gear oil pump located at the front in the oil pan and attached to the cylinder block. The oil pump is driven by a chain drive from the crankshaft.

Fig. 6. Renault Logan oil pump drive
1 - accessory drive pulley; 2 - the front cover of the cylinder block; 3 - the leading sprocket of the pump drive; 4 - drive chain; 5 - oil pump; 6 - crankshaft; 7 - the block of cylinders
The drive sprocket for the pump drive is mounted on the crankshaft under the front cover of the cylinder block. A cylindrical belt is made on the sprocket, along which the front crankshaft oil seal works. The sprocket is installed on the crankshaft without interference and is not secured with a key.
When assembling the Renault Logan engine, the pump drive drive sprocket is clamped between the timing pulley and the crankshaft shoulder as a result of tightening the package of parts with the accessory drive pulley bolt.
The torque from the crankshaft is transmitted to the sprocket only due to the frictional forces between the end surfaces of the sprocket, toothed pulley and crankshaft.
The oil receiver of the K7M engine is made in one piece with the cover of the oil pump housing. The cover is fastened with five screws to the pump casing. Pressure reducing valve located in the pump casing cover and kept from falling out by a spring clip.
The oil from the pump passes through the oil filter and enters the oil line in the cylinder block. Oil filter- full-flow, non-separable.
From the line, the oil goes to the main bearings of the crankshaft and further, through the channels in the crankshaft, to the connecting rod bearings. Through a vertical channel in the cylinder block of the Renault Logan engine, oil from the line is supplied to the cylinder head - to the middle camshaft support.
An annular groove is made in the middle bearing journal of the camshaft, along which the oil passes to the hollow bolt of the rocker arm shaft.
The rocker arms are made from holes through which oil is sprayed onto the camshaft cams. From the cylinder head, oil flows through vertical channels into the sump of the K7M engine.
The crankcase ventilation system is closed, forced, with gas extraction through an oil separator (in the cylinder head cover), which cleans the crankcase gases from oil particles.
Gases from the lower part of the crankcase enter through the internal channels in the cylinder head into the head cover and then, through two hoses (the main circuit and the idle circuit), enter the intake pipe of the Renault Logan engine.
Through the hose of the main circuit, blow-by gases are discharged at partial and full loads into the space in front of throttle.
Through the hose of the idle circuit, crankcase gases are discharged into the space behind the throttle valve both at partial and full load modes, and at idle speed.
Renault Logan engine with auxiliary units (front view along the vehicle):
1 - air conditioner compressor;
2 - accessory drive belt;
3 - generator;
4 - power steering pump;
5 - oil level indicator (oil dipstick);
6 - cylinder head cover;
7 - ignition coil;
8 - spark plugs;
9 - cylinder head;
10 - thermostat housing;
11 - exhaust manifold;
12 - pipe of the coolant pump;
13 - oxygen concentration sensor;
14 - oil pressure sensor;
15 - technological plug;
16 - flywheel;
17 - cylinder block;
18 - oil pan;
19 - oil filter
Renault Logan cars are equipped with K7J and K7M engines. Both engines are identical in design and differ only in displacement. The K7J engine has a displacement of 1.4 liters, while the K7M engine has a displacement of 1.6 liters. The increase in the working volume is obtained due to the larger radius of the crankshaft crank and, consequently, the larger piston stroke.
Both engines are petrol, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, with an overhead camshaft.
The order of operation of the cylinders: 1-3-4-2, counting from the flywheel.
Power system - distributed fuel injection (Euro-2 toxicity standards).
The engine with gearbox and clutch form a power unit - a single unit, fixed in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal bearings. The right support is attached to the bracket on the upper cover of the timing belt, and the left and rear support to the gearbox housing.
The engine block is cast from cast iron, the cylinders are bored directly into the block. The nominal cylinder diameter is 79.5 mm.

Renault Logan engine (rear view along the vehicle):
1 - gearbox;
2 - crankshaft position sensor;
3 - inlet pipeline;
4 - sensor of absolute air pressure in the intake manifold;
5 - intake air temperature sensor;
6 - throttle assembly;
7 - idle speed regulator;
8 - oil filler cap;
9 - fuel rail;
10 - oil level indicator (oil dipstick);
11 - cylinder head;
12 - cylinder block;
13 - accessory drive belt;
14 - oil pan;
15 - knock sensor;
16 - support bracket for the intake manifold;
17 - starter;
18 - vehicle speed sensor
In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five crankshaft main bearing supports with removable covers, which are attached to the block with special bolts. The holes in the cylinder block for the bearings are machined with the covers installed, therefore the covers are not interchangeable and are marked on the outer surface to distinguish them (covers are counted from the flywheel side). On the end surfaces of the middle support, sockets are made for thrust half rings that prevent axial movement of the crankshaft.

Renault Logan power unit (right side view along the vehicle):
1 - accessory drive belt;
2 - auxiliary unit drive pulley;
3 - the guide tube of the oil level indicator;
4 - support bracket of the inlet pipeline;
5 - lower cover of the timing belt;
6 - inlet pipeline;
7 - throttle assembly;
8 - upper cover of the timing belt;
9 - oil filler cap;
10 - ignition coil;
11 - pulley of the power steering pump;
12 - generator;
13 - support roller;
14 - tensioner roller;
15 - air conditioner compressor pulley;
16 - oil pan
The liners of the main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft are steel, thin-walled, with an anti-friction coating applied to the working surfaces. Crankshaft with five main journals and four connecting rod journals. The shaft is equipped with four counterweights, cast in one piece. To supply oil from the main journals to the connecting rods, channels are used, the outlet openings of which are closed with plugs. At the front end (toe) of the crankshaft are installed: an oil pump drive sprocket, a timing gear (timing) drive pulley and an accessory drive pulley. There is a projection in the hole of the toothed pulley, which enters the groove on the toe of the crankshaft and fixes the pulley from turning. Similarly, it is fixed on the shaft and the accessory drive pulley.

Renault Logan power unit (left-side view in the direction of the car):
1 - gearbox;
2 - air conditioning compressor;
3 - oxygen concentration sensor;
4 - generator;
5 - thermostat housing;
6 - coolant temperature sensor;
7 - cylinder head;
8 - cylinder head cover;
9 - ignition coil;
10 - oil filler neck;
11 - fuel rail;
12 - throttle position sensor;
13 - throttle assembly;
14 - inlet pipeline;
15 - intake air temperature sensor;
16 - sensor of absolute air pressure in the intake manifold;
17 - cylinder block;
18 - crankshaft position sensor;
19 - vehicle speed sensor

Flywheel:
1 - wreath for the crankshaft position sensor;
2 - a crown for starting the engine
A flywheel is attached to the crankshaft flange with seven bolts. It is cast from cast iron and has a pressed-on steel ring for starting the engine with a starter. In addition, a ring gear for the crankshaft position sensor is provided on the flywheel.
Connecting rods - steel, I-section, processed together with caps. The covers are attached to the connecting rods with special bolts and nuts.
Piston pin - steel, tubular section. The pin pressed into the upper connecting rod head rotates freely in the piston bosses.
The piston is made of aluminum alloy. The piston skirt has a complex shape: in the longitudinal section it is barrel-shaped, in the transverse section it is oval. In the upper part of the piston, there are three grooves for the piston rings. The two upper piston rings are compression rings and the lower one is an oil scraper.

Renault Logan cylinder head (head cover removed):
1 - cylinder head fastening screw;
2 - camshaft support;
3 - valve spring;
4 - spring plate;
5 - crackers;
6 - lock nut;
7 - an adjusting screw;
8 - bracket;
9 - a camshaft pulley;
10 - valve rocker;
11 - bolt of fastening of an axis of rocker arms of valves;
12 - the axis of the rocker arms of the valves;
13 - thrust flange of the camshaft
The cylinder head is an aluminum alloy, common to all four cylinders. It is centered on the block with two bushings and secured with ten screws. A non-shrinkable metal gasket is installed between the block and the head. There are five camshaft bearings (bearings) on the top of the cylinder head. The supports are made one-piece, and the camshaft is inserted into them from the timing drive side. The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft.
A groove is made in the extreme bearing journal of the camshaft (from the flywheel side), into which a thrust flange enters, which prevents axial movement of the shaft. The thrust flange is attached to the cylinder head with two screws. From above to the camshaft supports, the valve rocker shaft is attached with five bolts. The rocker arms are held against displacement along the axis by two brackets, which are fastened with the rocker arm axis bolts. Screws are screwed into the rocker arms, which serve to adjust the thermal clearances in the valve drive 5.
The adjusting screws are secured against loosening with locknuts. The valve seats and guides are pressed into the cylinder head. On top of the valve guides, the valve stem seals are put on. The valves are made of steel, arranged in two rows, inclined to the plane passing through the axes of the cylinders. In front (in the direction of the vehicle) there is a row of exhaust valves, and in the back there is a row of intake valves. The inlet valve disc is larger than the outlet valve.
The valve is opened by a rocker, one end of which rests on the camshaft cam, and the other, through an adjusting screw, on the end of the valve stem. The valve is closed by a spring. With its lower end, it rests on a washer, and with its upper end, on a plate, which is held by two crackers. The folded crackers on the outside have the shape of a truncated cone, and from the inside they are equipped with persistent collars that go into the groove on the valve stem

Renault Logan oil pump:
1 - driven sprocket of the drive;
2 - pump casing;
3 - pump casing cover with oil receiver
Engine lubrication - combined. The main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft and the bearings of the camshaft are lubricated under pressure. Other engine components are spray lubricated. The pressure in the lubrication system is generated by a gear oil pump located at the front in the oil pan and attached to the cylinder block. The oil pump is driven by a chain drive from the crankshaft.

Renault Logan oil pump drive (oil pan removed):
1 - accessory drive pulley;
2 - the front cover of the cylinder block;
3 - the leading sprocket of the pump drive;
4 - drive chain;
5 - oil pump;
6 - crankshaft;
7 - the block of cylinders
The drive sprocket for the pump drive is mounted on the crankshaft under the front cover of the cylinder block. A cylindrical belt is made on the sprocket, along which the front crankshaft oil seal works. The sprocket is installed on the crankshaft without interference and is not secured with a key. When assembling the engine, the pump drive drive sprocket is clamped between the timing gear pulley and the crankshaft shoulder as a result of tightening the package of parts with the accessory drive pulley mounting bolt. The torque from the crankshaft is transmitted to the sprocket only due to the frictional forces between the end surfaces of the sprocket, toothed pulley and crankshaft.
When loosening the fastening bolt of the accessory drive pulley, the drive sprocket of the oil pump drive may begin to turn on the crankshaft and the oil pressure in the engine will drop.
The oil receiver is made in one piece with the cover of the oil pump housing. The cover is fastened with five screws to the pump casing. The pressure reducing valve is located in the cover of the pump housing and is kept from falling out by a spring clip.
The oil from the pump passes through the oil filter and enters the oil line in the cylinder block. The oil filter is full-flow, non-separable. From the line, the oil goes to the main bearings of the crankshaft and then, through the channels in the crankshaft, to the connecting rod bearings. Through a vertical channel in the cylinder block, oil from the line is supplied to the cylinder head - to the middle support of the camshaft.
An annular groove is made in the middle bearing journal of the camshaft, along which the oil passes to the hollow bolt of the rocker arm shaft. Further, the oil, through a hollow bolt, enters the channel made in the rocker arm axis, and from there to the rocker arms and through other hollow axle bolts to the rest of the camshaft bearings. The rocker arms have holes through which oil is sprayed onto the camshaft cams. From the cylinder head, oil flows through vertical channels into the oil sump.
The crankcase ventilation system is closed, forced, with gas extraction through an oil separator (in the cylinder head cover), which cleans the crankcase gases from oil particles. Gases from the lower part of the crankcase enter through the internal channels in the cylinder head into the head cover and then, through two hoses (the main circuit and the idle circuit), enter the engine intake manifold.
Through the hose of the main circuit, blow-by gases are discharged at partial and full loads into the space in front of the throttle valve.
Through the hose of the idle circuit, crankcase gases are discharged into the space behind the throttle valve both at partial and full load modes, and at idle speed.
The control, power supply, cooling and exhaust systems are described in the respective chapters.
Renault Logan cars are reliable and economical family cars. Renault Logan has the most optimal engine specifications, which allows the car to be the best in its class of budget compact cars. Renault Logan is produced with a gasoline and diesel engine type. Fuel consumption in a petrol-fueled engine is 7.3 liters per 100 km in the combined cycle. Fuel consumption in a car running on a diesel engine is only 4.5 liters on the combined cycle. It is also allowed to install gas equipment on the car.
The general concept of both gasoline and diesel engines Renault Logan was about economy, low price and low-quality fuel. Most Renault Logan, common in Russia, drive gasoline engines such as Renault K7J, Renault K7M. Renault K7J has a displacement of 1.4 cu. liters and power 75 horsepower. The motor torque is 112 Nm and 3000 rpm, and it develops up to 5500 rpm. Renault K7M is produced with a volume of 1.6 cubic meters. liters, with a capacity of up to 87 horsepower and a torque of 3000 rpm. The difference in torque power depends on the environmental class of the motor. Modern versions gasoline engines Renault Logan is not produced as powerful, they have lost a few horsepower and nanometers of torque.
Since 2009, the manufacturer began to install Renault K4M engines with 4 valves per cylinder on Renault Logan.
This motor is somewhat simplified for the ability to use 92 brands of gasoline. The motor has a power of 102 horsepower, and in cars with automatic transmission gears, this figure is 103 horsepower, with a torque of 147 Nm and over 5000 rpm. The K4M engine is of a more modern design than the previous Renault Logan 8-valve valves. There are already hydraulic lifters, and not one coil for all cylinders is responsible for the ignition, but individual ones. Gasoline engines Renault Logan are reliable and capable of covering 300 thousand km without repairs and breakdowns with the planned maintenance... All Renault Logan engines run on 92 gasoline. The engine can be flashed for 95 gasoline.
The new Renault Logan models are powered by a more economical diesel engine.
The engine displacement is 1.5 cubic meters. liters. At the same time, the motor has excellent draft force and torque of 240 Nm. The motor allows the car to accelerate from the start to a speed of 100 km / h in just 10.4 seconds, while on gasoline models this figure is 13.7 seconds. There are modifications diesel engines with a volume of 2 cubic meters. liters. Engines are powerful, economical and environmentally friendly. They are provided with many technologies to reduce the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere.