Volkswagen-Audi cars are quite common in Russia. One of the features of these machines is their turbocharged engines. And if earlier the turbine could be found only on diesel engines, then "VAG" uses it everywhere on gasoline engines.
The purpose of the modernization is to maximize the technical characteristics of the unit while maintaining its working volume. Since fuel efficiency is important today, it is impossible to endlessly increase the volume of the combustion chamber. Therefore, carmakers go to different tricks. A striking example of such work is the TSI engine. What is it and what are the features of this power plant? Consider in our today's article.
Characteristic
The TSI engine is a petrol power unit that is used in Volkswagen, Skoda and Audi vehicles. The characteristic difference between the TSI engine is the presence of a double turbocharging and a direct fuel injection system (not to be confused with the Common Rail). Having developed a special design, German engineers have achieved high fuel efficiency of the unit with good technical characteristics.
The first TSI model appeared in 2000. This abbreviation literally translates as "double pressurized stratified injection".
Line of aggregates
It is quite extensive, and motors with the same displacement can produce different power. A prime example of this is the 1.4-liter TSI engine. 122 horsepower is far from the borderline. The concern also produces 1.4 TSI engines with 140 and 170 horsepower. How is this possible? It's simple: the differences lie in the pressurization technology:
- when using a single turbocharger, the TSI 1.4 engine power varies from 122 to 140 horsepower;
- with the use of two turbines, the power increases to 150-170 forces. This changes the software of the electronic engine control unit.

And all this on an engine with a working volume of 1.4 liters! But this is far from the only motor in the lineup. There are different variations of TSI engines:
- 1.0 TSI. This is the youngest motor. It is equipped with one turbine and develops 115 horsepower. The liter TSI engine has only three cylinders at its disposal.
- 1.4. We have already talked about these motors above. There are five engine variations in the lineup with power from 122 to 170 horsepower. All cylinders are located in one row.
- 1.8. These motors have three modifications. The power of this power plant can range from 152 to 180 horsepower.
- 2.0. These units develop power from 170 to 220 forces. The engine block is in-line, four-cylinder (as in the previous two units).
- 3.0. This is the flagship engine used in the Volkswagen Tuareg. It is a V-type six-cylinder engine. Depending on the degree of boost, its power can range from ЗЗЗ to 379 horsepower.

As you can see, the line of power units is quite extensive.
Device
It is worth noting that the TSI engines have been significantly redesigned. So, an aluminum block of cylinders, a modified intake and exhaust system, as well as an upgraded fuel injection system are installed here. However, first things first.
Blowers
The turbine is the main element that achieves such high performance. Superchargers on TSI motors are located on different sides of the block. The mechanism is powered by the energy of the exhaust gases. The latter set in motion the impeller, which, through special drives, pumps air into the intake manifold. Note that conventional turbocharged engines have a lot of disadvantages. In particular, this is the effect of the turbo lag - the loss of torque of the internal combustion engine at certain speeds. TSI motors do not have this disadvantage due to several superchargers. One works at low revs, and the second is connected at high revs. This is how the maximum torque is realized in a fairly wide range.
How does boost work?
Depending on the number of revolutions of the crankshaft, the following modes of operation of this system exist:
- Naturally aspirated. In this case, the turbine is not used. The engine speed does not exceed one thousand per minute. The throttle control valve is closed.
- Mechanical blower operation. This mechanism is activated when the revolutions are from one to two and a half thousand per minute. The mechanical supercharger helps provide good torque when starting from a standstill.
- Cooperative work of the turbine and the supercharger. This happens at a speed of two and a half to three and a half thousand.
- Turbocharger operation. The blower no longer starts up. Supercharging is provided only by the turbine impeller at a speed of three and a half thousand and above.

With an increase in the number of revolutions, the air pressure also increases. So, in the second mode, this parameter is about 0.17 MPa. In the third, the boost pressure reaches 0.26 MPa. At high rpm, the pressure level decreases slightly. This is done in order to prevent the detonation effect (spontaneous ignition of the gasoline mixture, which is accompanied by a characteristic blow to the piston crown). When the turbocharger is operating, the pressure level is 0.18 MPa. But this is enough to provide high torque and power when driving at speed.
Cooling system
Since the engine is under constant load, it needs good cooling.

So, the system has pipes that go through the intercooler. Thanks to this, cold air enters the cylinders. This ensures a more complete combustion of the mixture and contributes to an increase in engine dynamics.
Injection system
The TSI engine has an upgraded injection system. It is of the immediate type. Thus, the fuel enters the chamber immediately, bypassing the classic fuel rail. As noted by reviews, the work of direct injection is felt when accelerating. The car literally blows up from the "bottom". But the use of such an injection system is aimed not only at increasing the efficiency and power of the engine, it helps to reduce engine fuel consumption.
Cylinder block
The TSI engine features a lightweight aluminum cylinder block. The use of such an alloy significantly reduced the mass of the motor. On average, such a block weighs 14 kg less than a cast iron block. Also, the design uses other camshafts hidden behind a plastic cover. Thus, high operational performance of this ICE is achieved.
Problems
What problems do TSI engines have? One of the common diseases of these power plants is increased oil consumption. Moreover, the oil burner is not uncommon, even on new engines. What do the reviews say about the 1.4 TSI engines? These units consume up to 500 grams of oil per 1000 kilometers. That's quite a lot. Owners often need to check the level with a dipstick. If you miss the moment, you can catch oil starvation, which is fraught with a decrease in the resource of the TSI engine, namely its piston group. Can this problem be solved? Unfortunately, this is an "incurable disease" of all TSI engines, so the owner can only regularly monitor the dipstick and take a bottle of oil with him for refilling.

Another problem that put an end to the reliability of the 1.4 TSI engine is the failure of the turbine. It is often "showered" with oil, and by 80 thousand, bearing play appears. The turbine is not able to pump air under the required pressure, due to which the dynamics of consumption deteriorates and the nature of the behavior of the car changes. The cost of repairing a supercharger is about 60 thousand rubles, and there are several such turbines in the engine.
The next pitfall that questions the reliability of TSI engines is the gas distribution mechanism. They are powered by a chain that stretches frequently. The reason for this was the excessively high loads. In recent years, a German manufacturer has started to install a belt drive. According to the manufacturer, its strength has doubled. This somewhat improved the situation, however, there are many cars with the old timing chain left on the market.

How long does a TSI engine last? According to the manufacturer, its resource is about three hundred thousand kilometers. However, in practice, these motors run 150-200 kilometers. What significantly aggravates the situation is the aluminum block. It practically defies repair. There are no usual wet sleeves that could be replaced, so in case of failure, the TSI motor is easier to replace with a new one, which, by the way, is quite expensive.
Conclusion
So, we found out what the TSI engine is. The idea of creating this motor is not bad. The Germans strove to make a powerful and efficient engine, to get maximum efficiency from it. However, in pursuit of ideal characteristics, the engineers did not take into account a lot of nuances that were already corrected during the serial production of engines. Should you buy a car with such an engine? Experts give a negative answer, since the resource of these motors is really small. Chain drive problems are also common. Despite the high performance and low fuel consumption, you should refrain from buying such a car. The owner may be faced with unforeseen renovations and a fairly serious investment.
Many of you, dear readers (who are interested in German cars), sometimes when choosing for example volkswagen or its subsidiary skoda, come across such a question. What is TSI engine? After all, these brands have ordinary units and there are those with an incomprehensible abbreviation - TSI. I also asked this question and dug up such information ...
Everyone has heard about ordinary ones (Volkswagen and Skoda), as well as (AUDI), but TSI engines remain a mystery for the Russian consumer. What kind of motor is this? There are many sayings, especially in a drunken company, there is always a kind of connoisseur (who knows everything and has heard everything). I myself once thought it was a sinful thing - that this is a diesel option. I thought so because - with a smaller volume, it gives out more power than, for example, a simple turbocharged unit. But no - it's not diesel.
The brightest representative of the class is the 1.4-liter version of the Volkswagen company. How many awards and critical acclaims he received well, just an ideal among turbines!
Definition
TSI engines - These are gasoline units with double turbocharging (which also contain mechanical compressors), a system of direct "stratified" fuel injection. The structure is much more complex than a conventional turbocharged engine, but it should be noted that reliability, power and efficiency are at a very high level. It is practically devoid of flaws.
If you disassemble the abbreviation, there are several definitions. One since 2000 (that's when it was developed) - Twincharger Stratified Injection - translation (double supercharging, stratified injection), but later, around 2008, another translation appears Turbo Stratified Injection - (turbocharging, stratified injection), that is, the value of "double" is removed, it is during these years that the production of power units with one supercharger begins
Line of motors
You know many times I have witnessed that many argued - but the 1.4-liter engine, how many horses does it have? One says that it is 122, another 140, the third is generally 170 !!! How is this possible? It's just that this 1.4-liter unit became a great testing ground for the company, it was from it that all other variations from 1.0 to 3.0 grew. Indeed, it is 1.4 that now has a lot of variations, if I am not mistaken about 5 - 6.
Using his example (1.4), I will tell you how the Germans do it:
- One turbine. Variations 122 and 140 hp - differences in turbocharger power and firmware
- Turbine and compressor. Variations 150 - 160 - 170 HP - here either the power or the turbocharged supercharger changes, and of course the software (which is sewn into)
This situation is almost in the entire line, with the exception of the 1.0 TSI engine, it was originally developed only with a turbocharger - it is installed on small cars such as Volkswagen UP, or on hybrid versions. I have prepared a small plate for you, look
 All power units in stock are shown here, that is, the official software is flooded, if you change the configuration or firmware, you can squeeze out much more power.
All power units in stock are shown here, that is, the official software is flooded, if you change the configuration or firmware, you can squeeze out much more power.
Device
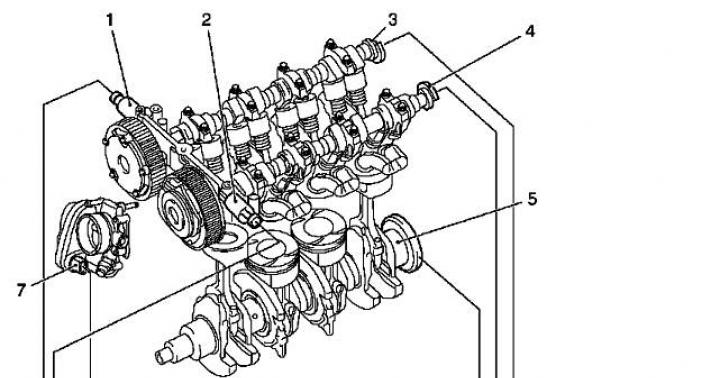
I will not go deep into the structure, but I will try to touch on the important elements and differences. To get started, take a look at the main blocks, here is a small diagram.

The unit has been significantly redesigned, especially worth noting - two superchargers, a new cooling system, fuel injection, a lightweight engine block. Now in order.
1) Mechanical compressor and turbocharger, the main differences

The device is such that they are located on opposite sides of the block. A conventional compressor uses the energy of the exhaust gas (located on one side). The exhaust gases themselves spin the turbine wheel, then, through special drives, compressed air is pumped into the engine cylinders (he wrote about a simple turbocharged version). The operating principle of the old type of motor is more efficient than that of a simple gasoline engine, but not as efficient as that of the TSI. A simple turbocharged unit is not very effective at idle and low speeds, the so-called "" effect is manifested (when full power appears only from 3000 rpm and above), that is, you always need to gas.
What can not be said about TSI. The only difference is that it also contains a mechanical compressor (on the other hand), which operates at low speeds. In this way, compressed air is always pumped (through special devices). Thanks to this mechanical compressor - the power does not drop, even from the bottom there is excellent traction, the "turbo pit" effect is defeated!
An excellent symbiosis of work: a mechanical supercharger on the "bottom" of the usual classic TURBO "on top", no power failures!
There are also improvements here. The concept of "liquid cooling" appears (conventional turbo variants are cooled only with air). The cooling system has pipes that go through. Due to this, the main air is forced into the cylinders, the pressure indicator is higher. The result is a uniform filling of the combustion chamber with a fuel mixture and an increase in dynamics. Already at 1000 - 1500 rpm we get the declared 210 Nm. Here is a small diagram of the cooling system, you can see the location of the pipes.

3) Fuel injection
A very interesting system. Firstly, the fuel is fed directly into the engine cylinders (bypassing the fuel rail), and secondly, mixing with air occurs "layer by layer" due to which combustion is achieved with high efficiency. These two factors allow for a slight increase in power and lower fuel consumption. Here is a diagram of the main elements of the fuel system.
 4) Lightweight unit
4) Lightweight unit
It should be noted that the engineers fought to reduce the weight of the unit unit. And you know, we managed to remove about 14 kilograms - a significant indicator. We used a new design for the placement of the block itself and the head, new camshafts and a plastic cover.

TSIs have proven to be very efficient motors - with a relatively small volume, very high horsepower values can be achieved. So the usual turbocharged type from Volkswagen, with a volume of 1.2 liters, has a power of about 90 hp, TSI - with the same volume, it can produce about 102 hp.
Second generation EA211 and EA888 GEN.3
Since 2013, the TSI engine line has been updated, many components have been redesigned that were previously considered not strong. So the main "Achilles' heel" was the timing chain.

She did not walk for a long time, especially in variations 1.2 - 1.4, it just stretched and torn at a run of 50 - 70,000 km (from a high load and high torque). Now it has been removed and the timing belt has been installed, they do not run much longer, but it is easier to change and easier to change, the difference in operation is about three times. For 1.8-2.0, the chain mechanism was significantly strengthened, the strength doubled.
The engine warm-up system was also redesigned, the predecessor (EA111 and EA888 GEN.2) took a long time to warm up. Now the problem is almost solved. There have been improvements and turbines. However, the "maslozhor" remained, the oil consumption can reach up to 5 liters per 10,000 km, so it is important to monitor the level.
Not everyone knows what TSI is and how this abbreviation stands. We will talk about this today.
What is TSI
The TSI engine is a gasoline-fueled unit featuring a "twin turbocharging" system. The translation of the abbreviation TSI reads as follows - an engine with turbocharging and fuel injection in layers.
A distinctive feature of the TSI design is the placement of the turbocharger on one side and the system responsible for mechanical compression on the other. The use of energy from the exhaust gases allows the power of a conventional turbo engine to be increased. This is possible due to the fact that the exhaust gases start the turbine wheel and forcefully pump and compress the air thanks to the drive system. Such a system shows greater efficiency than traditional ones.
What's improved in TSI engines
Recognized by experts and consumers, as evidenced by numerous awards. For three years (from 2006 to 2008), this system won the Engine of the Year award at the Engine of the Year competition.
Using the concept of minimization, the essence of which is that a smaller engine with low gasoline consumption produces the greatest power. Reducing the working volume made it possible to increase efficiency, while reducing friction losses. The small volume makes the engine and the vehicle lighter. Such technological solutions have become an integral part of TSI.
Video showing how the TSI engine works:
Combining drive and economy... The initial goal of the developers was to create economical engines with high power and reduced CO2 emissions.
Large RPM interval... TSI systems are configured so that when the crankshaft rotates at a frequency in the range from one and a half thousand to 1750 revolutions per minute, then the torque remains the highest, which has a good effect on how much gasoline is saved when the car is running, and on the power of the car. As a result, the driver gets maximum power over a wide rev range. TSI engines are perfectly compatible with transmissions with gear ratios that are much larger, which has a positive effect on.

Optimization of mixture formation, which was achieved due to the specially developed design of the high-pressure nozzle with 6 holes. The injection system is tuned so that it provides more efficiency in the process of gasoline combustion.
Intermediate cooling for greater dynamics... Another distinguishing feature of the unit is the presence of an intercooler for liquids, which has a system in which it circulates independently. This cooling allows you to reduce the volume of air that is pumped, due to which the boost pressure readings rise faster. As a result, due to the small delays of the turbo effect and the level of optimal filling of the combustion chamber, an increase in dynamics is achieved. TSI, with a declared power of 90 kW, does not have a turbo lag without an auxiliary compressor. Already at the 1500 rpm mark, the highest torque data of 200 Nm can be obtained.

Aspiration in TSI
Turbocharging and fuel injection... The TSI system uses a special technology that has made it possible to obtain the highest level of torque and the greatest power for a car, despite the fact that the engine has a rather small volume: fuel injection with turbocharging or combined supercharging using a turbocharger and compressor. In this design, fuel combustion is more efficient, due to which the TSI's power exceeds that of traditional atmospheric engines.
A turbocharger combined with a compressor has a good effect. The use of another compressor made it possible to smooth out the turbo lag effect that occurs due to the creation of a sufficiently high boost pressure by the turbocharger when the rev range is higher.

Boost pressure indicators. The Roots mechanical compressor is started by means of a belt drive crankshaft. In this case, the force level with which the boost occurs starts at the smallest rev range. This approach provides high traction and torque performance in a large rev range.
Dual supercharging, which is used in engines of this type, an efficient injection system, together with the highest pressure indicators with which fuel is injected, and the use of six-flow nozzles, allow TSI engines to save gasoline, which is spent. Today, Volkswagen cars from the Golf plus, Golf and Jetta ranges, Touran models and newer models already have a turbocharged engine.

Revolutionary innovative technology
Today Volkswagen is the only manufacturer that carries out the serial installation of engines of this type, equipped with a double supercharging in conjunction with a stage-by-stage injection, in cars of its own production. The placement of the compressor and turbocharger increases the pressure force with which the boost occurs. That is, an engine with a displacement of 1.4 liters is able to develop up to 125 kW (or 170 hp), which is a record in the automotive industry among four-cylinder engines.
Save gasoline thanks to reduced weight... The new TSI engine models, thanks to a number of improvements, weigh 14 kg less than the twin-turbocharged engines of the same type. Innovations include: design optimization of the block head and lighter weight of its cover, weight reduction by 304 grams of all camshafts.
Video about the operation of a turbocharged internal combustion engine:
It is only logical that the complexity of the design and engine improvements have influenced. However, the insignificant rise in price fully compensates for the increased power indicators and a decrease in the amount of fuel consumed.
TSI engine ( Turbo Stratified Injection, literally - turbocharging and stratified injection) combines the latest achievements of design ideas - direct fuel injection and turbocharging.
The Volkswagen concern has developed and offers on its cars a line of TSI engines that differ in design, engine size, and power indicators. In the design of TSI engines, the manufacturer has implemented two approaches: double charging and simply turbocharging.
The abbreviation TSI is a patented trademark of the Volkswagen Group.
Dual charging is carried out, depending on the needs of the engine, by two devices: a mechanical supercharger and a turbocharger. The combined use of these devices makes it possible to realize the rated torque over a wide range of engine speeds.
The engine uses a mechanical Roots supercharger. It consists of two rotors of a certain shape, placed in a housing. The rotors rotate in opposite directions, which provides air intake on one side, compression and discharge - on the other. The mechanical supercharger is belt driven from the crankshaft. The drive is activated by a magnetic clutch. To regulate the charge pressure, a control damper is installed parallel to the compressor.
The twin supercharged TSI engine has a standard turbocharger. The charge air is cooled by an air-type intercooler.
The efficient operation of double boost is ensured by the engine management system, which, in addition to the electronic unit, combines input sensors (pressure in the intake manifold, boost pressure, pressure in the intake manifold, regulating flap potentiometer) and actuators (magnetic clutch, control flap servomotor, boost pressure limiting valve, turbocharger recirculation valve).
The sensors monitor the boost pressure at various points in the system: after the mechanical supercharger, after the turbocharger and after the intercooler. Each of the pressure sensors is combined with air temperature sensors.
Magnetic clutch it is switched on by signals from the engine control unit, at which voltage is applied to the magnetic coil. The magnetic field attracts the friction disc and closes it to the pulley. The mechanical compressor starts rotating. The compressor operates as long as voltage is applied to the magnetic coil.
Servo motor turns the regulating flap. When the damper is closed, all intake air flows through the compressor. The boost pressure of a mechanical compressor is controlled by opening the damper. In this case, part of the compressed air is fed back to the compressor, and the boost pressure is reduced. When the compressor is not running, the damper is fully open.
Boost pressure limiting valve is triggered when the energy from the exhaust gas builds up excess boost pressure. The valve operates the vacuum actuator, which in turn opens the bypass valve. Part of the exhaust gas flows past the turbine.
Turbocharger recirculation valve ensures that the system operates at forced idle (with the throttle valve closed). It prevents overpressure between the turbocharger and the closed throttle valve.
The principle of operation of the double turbocharged TSI engine
Depending on the speed of the engine crankshaft (load), the following modes of operation of the dual boost system are distinguished:
- naturally aspirated mode (up to 1000 rpm);
- operation of a mechanical supercharger (1000-2400 rpm);
- joint operation of a supercharger and a turbocharger (2400-3500 rpm);
- turbocharger operation (over 3500 rpm).
At idle, the engine runs naturally aspirated. The mechanical blower is off, the control flap is open. The exhaust energy is low and the turbocharger does not generate boost pressure.
As the speed rises, the mechanical blower turns on and the control damper closes. The boost pressure is mainly generated by a mechanical supercharger (0.17 MPa). The turbocharger provides little additional air compression.
At a speed of rotation of the engine crankshaft in the range of 2400-3500 rpm, the boost pressure is created by a turbocharger. The mechanical supercharger is connected when necessary, for example, when accelerating rapidly (sharp opening of the throttle valve). The boost pressure can be up to 0.25 MPa.
Further, the work of the system is carried out only by the turbocharger. The mechanical blower is off. The control flap is open. To prevent detonation with an increase in the number of revolutions, the boost pressure drops slightly. At a rotational speed of 5500 rpm, it is about 0.18 MPa.
Turbocharging TSI engine
In these engines, charging is carried out exclusively by a turbocharger. The design of the turbocharger ensures that the nominal torque is achieved even at low engine speeds and that it is maintained in a wide range (from 1500 to 4000 rpm). Outstanding characteristics of the turbocharger are obtained by minimizing the inertia of the rotating parts: the outer diameter of the turbine and compressor impeller is reduced.
System boost control is traditionally done with a bypass valve. The valve can be pneumatic or electric. The operation of the pneumatic drive is ensured by the boost pressure limiting solenoid valve. The electric drive is represented by an electric guiding device, consisting of an electric motor, a gear train, a linkage mechanism and a position sensor of the device.
A turbocharged engine uses a liquid-cooled charge air system as opposed to a dual-charge engine. It has a circuit independent of the engine cooling system and forms a dual-circuit cooling system with it. The charge air cooling system includes: charge air cooler, pump, radiator and piping system. The charge air cooler is located in the intake manifold. The cooler consists of aluminum plates through which the pipes of the cooling system pass.
The charge air is cooled by a signal from the engine control unit by turning on the pump. The flow of heated air passes through the plates, gives them heat, and they, in turn, give it to the liquid. The coolant moves along the circuit with the help of a pump, is cooled in the radiator and then in a circle.
TSI-branded cars have a special heart under the hood. This is the engine in which Volkswagen designers have applied the most modern technologies and research, translating them into production cars to change the characteristics of this type of engine.
What does the definition of TSI engine mean
Recently, a new TSI marking has appeared on many cars. This abbreviation denotes a new type of automobile engine with an improved design. The abbreviation TSI, which can be deciphered as Turbo Stratified Injection, when translated into Russian, it can be expressed approximately as "Turbo Layer Fuel Injection". Using this principle of fuel supply in TSI engines, the manufacturer managed to achieve high performance when operating the motors.
The main feature of TSI engines is the duplication of pressurization systems with a mechanical compressor and a turbine supercharger. This design makes it possible to achieve high performance in all modes of the engine robots and significant fuel savings due to the possibility of varying the fuel injection modes, due to this it is possible to achieve high efficiency.
Such engines have the following basic operating modes:
Compressor boost range as required.

At engine speeds up to 3500, a compressor is connected if necessary. All this is necessary when the motor runs constantly in this mode, and then strong acceleration follows. The inertia of the turbocharger leads to a delay in the creation of the required pressure (the so-called "turbo pit"). Therefore, a compressor is connected here, which creates the required inlet pressure in the shortest possible time.
Compressor constant boost range.
From idle speed up to 2400 engine revolutions, the mechanical compressor is constantly on. With such a difference in rpm, the boost pressure in the compressor is controlled by the intake manifold flap control unit.
Boost range for turbocharger only.
When the engine speed is over 3500, the turbine supercharger alone can create the required pressure. In this case, the charge air pressure is controlled by the charge pressure control solenoid valve.
 In addition to the dual supercharging system, the TSI engine has the specificity of the engine cooling system. It has two cooling circuits: a cylinder head with a turbine and a cylinder block with an intercooler.
In addition to the dual supercharging system, the TSI engine has the specificity of the engine cooling system. It has two cooling circuits: a cylinder head with a turbine and a cylinder block with an intercooler.
The main components of the engine, the improvement took place
The task of increasing engine power without significantly increasing its volume and weight, maintaining fuel efficiency, the design department of the Volkswagen Group managed to implement, making non-standard solutions.
Structurally, the TSI engine has features in comparison with other motors, namely double discharge - a mechanical compressor and a turbocharger. The base for the TSI engine was a four-cylinder power unit, which was equipped with a sequential fuel injection system, a mechanical supercharger of the Roots type, and a turbocharger.
Dividing the cooling system into two (one cools the engine head and exhaust manifold, and the other cools the cylinder block and liquid intercooler) effectively cools the charge air.

When one of the most important priorities for the car was determined - with lower volumes the highest power density - the design thought came to the idea of a boost. Why does an engine need two pressurization systems?
Each of the systems separately has its own disadvantages. So, the turbine does not work at low speeds. For its normal operation, the engine must be rotated up to 3000 rpm, that is, keep high revs all the time in order to avoid failures (so-called turbo pits). At high speeds, the efficiency of a mechanical compressor decreases, but at the bottom, it allows the motor to work with full efficiency. In transient modes, both systems duplicate each other, which gives a positive result, making it possible to remove the maximum torque from the engine. The first were mechanical (forced) blowers, which are driven by the engine's crankshaft.
But more use is found in the automotive industry, a supercharger driven by a turbine, which is affected by exhaust gases. When the load and the number of revolutions change, the engine ECU calculates how much air is needed to create the required torque and enters the cylinders. In this case, it determines whether the turbocharger is operating itself or whether a mechanical compressor should be added to the operation.
There are several operating ranges in TSI engines:
Naturally aspirated at minimum load.
In naturally aspirated mode, the control flap is fully open. The air that enters the engine enters through the turbocharger flap, which is controlled by the regulating control unit. At this time, the turbocharger is already running under the influence of the exhaust gases. Their energy is so low that a minimum boost pressure is created. In this case, the throttle valve opens at the request of the driver (by pressing the gas pedal), and a vacuum is created at the inlet to the cylinders.
Mechanical compressor and turbine supercharger for high loads and speeds up to 2400 rpm.
 When operating in this range, the air regulating flap is closed or slightly opened to regulate the pressure in the intake manifold. In this case, the compressor is put into operation through a magnetic clutch and is driven by a poly-V-belt drive (it sucks in air and compresses it). Compressed air is pumped by the compressor to the turbine supercharger. In this case, the air is additionally compressed. The compressor boost pressure is measured at the intake manifold by a pressure sensor and is changed by the control flap control unit. The total boost pressure is measured by the boost pressure sensor with the throttle valve fully open. A pressure of up to 2.5 bar is generated at the inlet to the cylinders.
When operating in this range, the air regulating flap is closed or slightly opened to regulate the pressure in the intake manifold. In this case, the compressor is put into operation through a magnetic clutch and is driven by a poly-V-belt drive (it sucks in air and compresses it). Compressed air is pumped by the compressor to the turbine supercharger. In this case, the air is additionally compressed. The compressor boost pressure is measured at the intake manifold by a pressure sensor and is changed by the control flap control unit. The total boost pressure is measured by the boost pressure sensor with the throttle valve fully open. A pressure of up to 2.5 bar is generated at the inlet to the cylinders.
Turbine blower and mechanical compressor operation at high loads and revs from 2400 to 3500 rpm.
When the engine is operating in this mode (for example, at a constant speed), the boost pressure is generated only by the turbine supercharger. When accelerating, the turbine would have worked with a delay and would not have been able to create the required air pressure in time (a turbo pit could occur). But to exclude this, the engine control unit connects the compressor via an electromagnetic clutch. This changes the position of the control flap, creating a corresponding boost pressure. This is how the mechanical compressor assists the turbine supercharger in creating the necessary air pressure for the engine to operate.
Working with a turbine supercharger.
 When the engine speed is over 3500 rpm, the turbine can create the required air pressure at any point of load. In this situation, the damper that regulates the air supply is fully open and fresh air is supplied directly to the turbine blower. Under these conditions, the exhaust gas pressure will be sufficient for the turbocharger to generate the required boost pressure. At the same time, it is completely open. The inlet is pressurized up to 2.0 bar. The pressure generated by the turbocharger is measured by the boost pressure sensor and is controlled by the boost pressure limiting valve.
When the engine speed is over 3500 rpm, the turbine can create the required air pressure at any point of load. In this situation, the damper that regulates the air supply is fully open and fresh air is supplied directly to the turbine blower. Under these conditions, the exhaust gas pressure will be sufficient for the turbocharger to generate the required boost pressure. At the same time, it is completely open. The inlet is pressurized up to 2.0 bar. The pressure generated by the turbocharger is measured by the boost pressure sensor and is controlled by the boost pressure limiting valve.
Dual charging is the simultaneous use of a mechanical compressor + a turbocharger. The compressor is a mechanical type blower that is connected through an electromagnetic clutch.
Mechanical compressor benefits:
- fast injection of the required pressure into the intake manifold;
Creation of more torque at low engine speeds;
Its connection occurs on demand;
It does not require additional lubrication and cooling.
Disadvantages of a mechanical compressor:
- power take-off from the motor,
The boost pressure is created depending on the speed of the crankshaft and then it is regulated, in this case, part of the work performed is again lost.
The turbocharger is constantly driven by the exhaust gases.
The advantages of this unit: high efficiency due to the use of energy from the exhaust gas. Disadvantages of a turbine supercharger:with a small working volume of the engine, the generated amount of exhaust gases is not enough to create boost pressure at low engine speeds and create a high turbine torque, high temperature load.
 Using a combined supercharging system, that is, combining a classic turbocharging and a mechanical one, the creators of the TSI engine reached maximum power indicators in all engine operating modes.
Using a combined supercharging system, that is, combining a classic turbocharging and a mechanical one, the creators of the TSI engine reached maximum power indicators in all engine operating modes.
Cooling system
Classic single-circuit cooling system. To improve the efficiency of the robots of the TSI engine, the designers divided the engine cooling system into two circuits to improve the quality of the engine and its systems.
The cooling system was divided into two modules: one circuit serves the exhaust manifold and the engine head (hot), the other (cold) cools the cylinder block and the charge air in the intercooler. These motors are equipped with a water intercooler, which replaced the air one. Due to this, the air that is forced into the cylinders has a higher pressure indicator. The result of this modernization is the uniform filling of the combustion chambers with a fuel-air mixture and an increase in the dynamics of the car. So, already at 1000 - 1500 rpm, we get a torque of about the declared figure of 210 Nm.
A dual-circuit cooling system is a scheme in which the circuits of the cylinder block and the head of the block are separated. In the cylinder head, coolant flows from the exhaust manifold to the intake manifold. Thus, a uniform temperature regime is maintained. This design is called transverse cooling. Also, the following changes have been made to the cooling system:
- the thermostat is made with two stages;
To cool the turbine when the engine is stopped, a coolant recirculation pump is installed;
The turbine supercharger is forced-cooled.
 Approximately one third of the engine coolant flows to the cylinder block, and the remaining 2/3 to the cylinder head to the combustion chambers. Advantages of a dual circuit cooling system:
Approximately one third of the engine coolant flows to the cylinder block, and the remaining 2/3 to the cylinder head to the combustion chambers. Advantages of a dual circuit cooling system:
- the cylinder block warms up more quickly, the temperature rises to 95 ° due to what remains in the block;
Reduction of friction in the crank mechanism due to an increase in temperature in the cylinder block;
Improving the cooling of the combustion chambers due to a temperature drop of about 80 ° in the block head; thus, an improvement in filling is achieved while reducing the possibility of detonation.
A special feature of the cooling system is the coolant distributor housing with a thermostat, which has two stages. With such a volume of coolant at high engine speeds, increased pressure occurs in the cooling system. Even under these conditions, the two-stage thermostat opens at the set time according to the required temperature.
When a single stage thermostat is installed, it would be necessary to overcome the high pressure and move the large thermostat plate. And therefore, due to the oncoming forces, the thermostat could only open at high temperatures.
In a two-stage thermostat, when the opening temperature is reached, the small plate will open first. Due to the small area, the forces that act on the plate are less, and the thermostat opens strictly in accordance with the temperature. After a certain stroke, the small poppet starts pulling the large one, fully opening the large coolant passage.
 When the TSI engine warms up, this system makes it possible to maintain the operating temperature in the engine in accordance with the specified parameters and to reduce fuel consumption and harmful emissions. To improve heating and reduce the possibility of overheating, it is necessary to intensively cool the hot cylinder head. In this case, the amount of coolant in the block head is twice the amount of fluid in the cylinder block, and the thermostats open at 95 ° and 80 °, respectively.
When the TSI engine warms up, this system makes it possible to maintain the operating temperature in the engine in accordance with the specified parameters and to reduce fuel consumption and harmful emissions. To improve heating and reduce the possibility of overheating, it is necessary to intensively cool the hot cylinder head. In this case, the amount of coolant in the block head is twice the amount of fluid in the cylinder block, and the thermostats open at 95 ° and 80 °, respectively.
The turbine is protected from overheating by an additional electrically driven auxiliary water pump, which makes the liquid circulate in a separate circuit after the engine stops for up to 1/4 hour. With this principle of operation, the service life of the turbine supercharger of the TSI engine is significantly increased.
Fuel is supplied via a variable fuel injection system. The advantage of this system is that the electric fuel pump, like the high pressure fuel pump, delivers as much gasoline as the engine needs. Thus, the electrical and mechanical power of the fuel pumps is reduced and fuel is saved.
For direct fuel injection, the injectors are installed directly in the cylinder head. Under high pressure, fuel is injected through them into the cylinders. Main task for injectors:they are obliged to spray efficiently and purposefully supply gasoline to the cylinders in a minimum period of time.
When starting a cold engine, the TSI engine is double-injected. This is done in order to warm up the catalyst when starting the engine. The first time is during the intake stroke, and the second time is when the engine crankshaft has not reached top dead center by about 50 ° during rotation. When the engine is operating under normal conditions, fuel is supplied during the intake stroke, and it is distributed evenly in the combustion chamber. The injectors installed on the TSI have 6 fuel injection ports.
 Thus, the direction of individual jets prevents the combustion chamber elements from wetting, providing a better distribution of the fuel-air mixture. In this case, the maximum value of the fuel injection pressure reaches 150 bar. This makes it possible to guarantee high-quality preparation of the fuel mixture and reliable atomization. In this case, there will be enough fuel even at maximum loads.
Thus, the direction of individual jets prevents the combustion chamber elements from wetting, providing a better distribution of the fuel-air mixture. In this case, the maximum value of the fuel injection pressure reaches 150 bar. This makes it possible to guarantee high-quality preparation of the fuel mixture and reliable atomization. In this case, there will be enough fuel even at maximum loads.
On TSI engines, fuel goes directly to the cylinders, and not to the intake manifold, mixture formation occurs "layer by layer", and thus there is a high-quality combustion with high efficiency. All these factors make it possible to slightly increase power and reduce fuel consumption.
It should be noted that the efforts of engineers to reduce the weight of the cylinder block have yielded results. The 1.2 L TSI engine block is cast from aluminum. Compared to the engine block, which is made of gray cast iron (such cylinder blocks are used in the TSI engine with a volume of 1.4 liters), the new cylinder block has reduced weight by 14.5 kg to 19.5 kg. The design of the new 1.2L TSI engine block with an open platen is identical to the cylinder block of the 1.4L TSI engine. The peculiarity of this scheme is that the inner wall of the cylinder block with liners does not have jumpers in the area where the cylinder block contacts the block head.
This design has its advantages:
- it reduces the possibility of the formation of air bubbles, in a system with dual-circuit cooling, they can create a problem for removing air from the engine cooling system.
By assembling the cylinder block and cylinder head into a single unit, cylinder deformations are reduced and a more homogeneous design is achieved when compared to a closed plate and web design.
 All this leads to a reduction in oil consumption, because the piston rings in this case better compensate for deformations. The cylinder block contains four liners made of gray cast iron with a profiled outer surface. This profile improves the connection between the cylinder block and the cylinder liners, thus reducing the deformation of the cylinder block. This technological solution made it possible to reduce the unevenness in the distribution of heat that appears between the liners and the aluminum block.
All this leads to a reduction in oil consumption, because the piston rings in this case better compensate for deformations. The cylinder block contains four liners made of gray cast iron with a profiled outer surface. This profile improves the connection between the cylinder block and the cylinder liners, thus reducing the deformation of the cylinder block. This technological solution made it possible to reduce the unevenness in the distribution of heat that appears between the liners and the aluminum block.
Advantages of the TSI engine
The advantages of motors with the abbreviation TSI include:
1. Design efficiency (with minimum fuel consumption it is possible to achieve maximum torque in a wider rpm range).
2. Due to the reduction in engine weight and displacement, friction losses are significantly reduced.
3. The fuel consumed by the engine is saved.
4. With improved characteristics of fuel combustion, the amount of harmful emissions into the environment is reduced.
 TSI are engines with direct fuel injection systems and twin turbocharging (contains a compressor and a turbine). Such engines are more complicated than conventional turbocharged engines, but they are more reliable, more powerful and more economical. They have practically no disadvantages.
TSI are engines with direct fuel injection systems and twin turbocharging (contains a compressor and a turbine). Such engines are more complicated than conventional turbocharged engines, but they are more reliable, more powerful and more economical. They have practically no disadvantages.
A feature of these motors is a two-stage supercharging, which consists of a turbine supercharger and a mechanically driven compressor. The TSI engine is full of modern technological solutions, but at the same time, proper care is required for its reliable operation. Therefore, you need to use high-quality consumables and fluids, to carry out maintenance on time. The components and assemblies included in the TSI engine and timely maintenance will more than pay off due to the savings in gasoline.
In order to reduce noise, this engine has an additional housing, which is made of sound-absorbing materials.
Engine use in our country
This engine is designed to run only on good fuel and only on excellent oils, we have to look for good fuel.
TO disadvantages of TSI engines that will be used in our conditions include:
- high requirements for the quality of fuels and lubricants - gasoline, oil, etc .;
Maintenance, which must be carried out regularly and only at authorized service centers;
These motors are sensitive to low ambient temperatures, which makes it difficult to operate in winter.
 But drivers who have experience in operating TSI engines notice that warming up at idle is not necessary - you can start driving without warming up with a cold engine. TSI engines with direct fuel injection and twin turbocharging are more sophisticated than conventional engines, but they are more reliable, more powerful and more economical.
But drivers who have experience in operating TSI engines notice that warming up at idle is not necessary - you can start driving without warming up with a cold engine. TSI engines with direct fuel injection and twin turbocharging are more sophisticated than conventional engines, but they are more reliable, more powerful and more economical.
One of the biggest drawbacks is that the engine does not warm up well when idling in winter. When driving, the engine reaches the set temperature for a long time. Therefore, for drivers who drive close distances, this will create a problem (you will have to drive with an unheated "stove" and endure the cold air blowing from the heater in frosty weather). The TSI engine does not create any other problems.
It should also be noted increased mechanical and thermal loads, double boost. All this forces manufacturers to constantly work on changing the design, to strengthen some of the engine components and assemblies. This complicates the very production and maintenance of such units.