For an ordinary person, the word "bithermic heat exchanger" sounds magically high-tech. Let's try to figure out what it is and how it works.
Wall-mounted boilers use 2 heating methods hot water for households needs:
1) DHW is heated in the same heat exchanger in which heating water (HW) is heated.
2) Heating water is heated in the primary heat exchanger, and heat exchange between the RH and DHW takes place in the secondary plate heat exchanger.
Let's look at what are the advantages and disadvantages of this or that method.
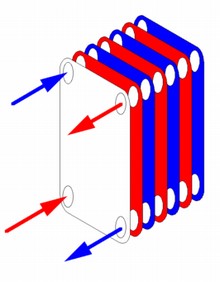
The figure schematically shows a bithermic heat exchanger. 1. DHW outlet 2. DHW inlet 3. Heating circuit flow 4. Heating circuit return
From the figure, we see that domestic water flows through the inner tubes, and heating water in the cavities between the inner tube and the outer one. Moreover, household water flows sequentially through all 6 pipes, and heating water flows through 3 in parallel in one direction and in three in parallel in the opposite direction.
Principle of operation: when there is no DHW flow, the pump works, the RH circulates through the system, heating up in the heat exchanger. When a DHW flow appears, the pump turns off, there is no circulation in the system, and DHW is heated in the heat exchanger.

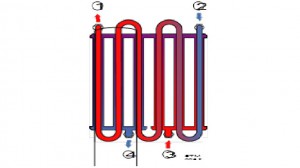
The top picture shows the primary heat exchanger manufactured by Mora Top. The figure on the right shows the secondary heat exchanger. Below is a functional diagram of the operation of a boiler with a secondary heat exchanger in the DHW heating mode.
Principle of operation: when there is no DHW flow, the pump works, the RH circulates through the system, heating up in the heat exchanger.
When the DHW flow appears, the pump continues to operate, the three-way valve transfers the RH flow from the heating system to the secondary heat exchanger in which heat exchange takes place between heating and utility water.
So, we figured out the principle of work. Now let's give the advantages and disadvantages of both methods of heating hot water.
Bithermic heat exchanger
Advantages:
- cheaper production (a bithermic heat exchanger is cheaper than two separate heat exchangers and a three-way valve)
- It takes up less space inside the boiler compared to a primary, secondary heat exchanger and a three-way valve with inlet pipes.
Flaws:
- During operation of the boiler in heating mode in the DHW circuit of the heat exchanger household. the water is heated to the same temperature as the RH. If the temperature in the heating system is set above 60 degrees, then when the tap is opened, water of the same temperature will flow, which can lead to burns. Because of this, on boilers with a bithermic heat exchanger, the temperature of the RH is programmatically limited to 75-77 degrees.
- At the time of using the DHW in the heating circuit, the coolant is motionless, and at the time of operation of the boiler for heating in the DHW circuit, the water is motionless. Accordingly, in the first case, the coolant, and in the second case, the water is heated to high temperatures without circulation, which leads to excessive formation of water stone on the heat exchange surfaces.
- It can be seen from the figure that the coolant circulates in one tube through 4 cavities in parallel. Also in parallel, it circulates in parallel through the 3 tubes of the heat exchanger. Accordingly, if at least one of the 12 cavities is clogged with scale to such an extent that the flow through it stops, then the coolant boils in this cavity. This is expressed in strong noises during the operation of the boiler. It is not always possible to wash such a heat exchanger even with the help of special equipment. The cost of replacing a heat exchanger often exceeds 50% of the cost of the boiler. In order to avoid fatal blockages of the heat exchanger, the bithermic heat exchanger must be flushed much more often.
- For a bithermic heat exchanger, the manufacturing process is more complicated than for a monothermal one. It has more joints, and therefore the likelihood of leaks is greater. There are also cases when a leak appears between the circuits inside the heat exchanger.
- A bithermic heat exchanger, unlike a monothermal one, is practically not repairable in the event of a leak.
Primary, secondary heat exchanger and three-way valve
Advantages:
- The presence of a secondary eliminates the overheating of hot water over 60 degrees, since heat exchange occurs in the secondary heat exchanger between the OV (maximum temperature 80 degrees) and hot water. This eliminates the risk of burns.
- In view of the fact that the DHW does not heat up above 60 degrees (in a bithermic heat exchanger up to 80) and heating occurs only at the moment when there is a flow through the second circuit (it always heats up in a bithermic one), scale formation in the secondary heat exchanger is many times slower than in bithermic ceteris paribus.
- Since there is no secondary circuit in the primary heat exchanger, the flow area of the heat exchanger tubes is larger and all tubes can be connected in series. This minimizes the chances of a complete blockage of the heat exchanger. And even a heat exchanger heavily clogged with scale can always be washed.
- Separately, each of the nodes is cheaper than a bithermic heat exchanger, and consequently, repairs in the event of a breakdown will be less expensive.
Flaws:
- This solution is more expensive, which is reflected in the final cost of the boiler.
- The three-way valve has mechanically coupled elements that increase the risk of breakage.
From all of the above, it follows that if the main criterion for choosing a boiler is not low price, then it is better to make a choice in favor of a boiler with a monothermal and secondary heat exchanger.
What is a bithermic heat exchanger? Which boiler is better - with a bithermic heat exchanger or two separate ones? We will try to answer this question in our article.
Bithermic heat exchanger- This is a type of boiler heat exchanger. A bithermic heat exchanger is necessary to ensure the heating of the heating coolant and running water for hot water supply, directly in the combustion chamber of the boiler. Structurally, a bithermic heat exchanger can be characterized by the term "pipe in a pipe" - in the section we see a pipe divided into several sectors. Also this model is called "double heat exchanger". In one part, the heating medium circulates, in the other - water for hot water supply. Special copper plates are attached to the tube - heat exchanger fins.
 The diagram shows clearly a bithermic heat exchanger in section. The inner pipe is designed for hot water, and the outer pipe for the heating system coolant. The bithermic design of the heat exchanger has its advantages and disadvantages. The use of a bithermic heat exchanger in the boiler makes it cheaper. There is no need to additionally install a three-way valve and a secondary heat exchanger. This reduces the cost of the boiler and increases the reliability of its operation. The disadvantage of a bithermic heat exchanger is the limited operation in DHW mode and the preparation of a smaller amount of hot water than in boilers with two heat exchangers. In addition, it is not recommended to use boilers with bithermic heat exchangers in areas where the water contains an increased amount of salts. This is due to the fact that due to the large temperature difference in
The diagram shows clearly a bithermic heat exchanger in section. The inner pipe is designed for hot water, and the outer pipe for the heating system coolant. The bithermic design of the heat exchanger has its advantages and disadvantages. The use of a bithermic heat exchanger in the boiler makes it cheaper. There is no need to additionally install a three-way valve and a secondary heat exchanger. This reduces the cost of the boiler and increases the reliability of its operation. The disadvantage of a bithermic heat exchanger is the limited operation in DHW mode and the preparation of a smaller amount of hot water than in boilers with two heat exchangers. In addition, it is not recommended to use boilers with bithermic heat exchangers in areas where the water contains an increased amount of salts. This is due to the fact that due to the large temperature difference in
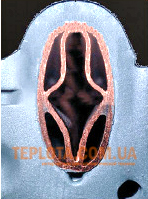
In heating and hot water circuits, the process of salt deposition occurs more intensively and the heat exchanger clogs more often. Water filters can partially prevent this problem, but still this does not give them an advantage. Despite the inherent disadvantages, boilers with a bithermic heat exchanger are the most popular devices on sale. Due to its low price and positive feedback about work, this technique holds the lead in sales of boilers. Catalog filters of the TEPLOTA KOM UA online store are able to limit the search among boilers based on various parameters. Among other things, you can restrict the display of only boilers with
Gas boilers are popular among consumers due to their small size, easy installation and reasonable price. It is worth noting the ease of operation of this device and the availability of fuel to ensure the functioning of the boiler. Our store offers to buy any model from a wide range of gas boilers with a variety of characteristics.
Gas boilers can be installed in two ways:
The first option has larger volumes and weight, as a rule, due to the cast-iron heat exchanger. It is advisable to use such a boiler in private homes, where it is possible to equip a separate office space under.
The wall-mounted boiler is a compact equipment that fits perfectly into the interior of the kitchen, bathroom (if there is a window). Due to the high level of modern design, such a boiler will harmoniously look in any style environment.
According to the purpose and power of operation, a gas boiler can be single-circuit or double-circuit, single-stage or two-stage, that is, operating in one or two modes. A single-circuit boiler is used only for heating, but.
Types of gas boilers
According to the principle of operation, gas boilers are divided into two groups:
- convection;
- condensation.
The first group of boilers is considered to be traditional equipment that produces heating by burning gas, while part of the heat leaves with flue waste. The principle of operation of such a boiler is simple, understandable, and the price is relatively low.
The second type of boilers was developed according to new technologies, which make it possible to more fully use the heat of combustion of gas. This allows you to get an efficiency of about 15-20 percent higher than that of the convection model. And this means corresponding fuel savings and getting cheaper heat. However, it is significantly higher than that of convection.
Many European and world-class companies are engaged in the development and production of gas boilers. Almost all modern models are equipped with a reliable automated protective system that does not require manual control, which is responsible for supplying fuel and maintaining the temperature in a given mode. Models equipped with a gas pressure controller are guaranteed against overheating, fire, and other similar failures, as it will immediately cut off the gas supply in the event of pressure loss, fuel leakage, or flame failure.
MoreTechnological progress in the segment of heating equipment is developing in different directions. Some manufacturers are betting on improving performance characteristics element base of aggregates, others promote latest devices automatic control, and still others at the basic level are also involved in the optimization of structures. The last group of developments includes a bithermic heat exchanger. What it is? In fact, this is a heating chamber capable of performing two different tasks - to prepare water directly for heating, and for the needs of hot water supply, that is, for domestic consumption.
General information about the bithermic heat exchanger
Classic heat exchangers for boilers provide for the separation of heating chambers. That is, one chamber is intended for servicing the heating circuits - as a rule, the main one, and for hot water supply - a secondary radiator. This design has many advantages, however, against the background of the combined heating chambers, its weak sides. In this case, it would be wrong to assume that in the second case the water is mixed - such a principle does not allow a bithermic heat exchanger either. What is it in terms of approach to water maintenance? This is the same radiator equipment, but with a common housing, which contains both chambers for heating the coolant and compartments for preparing domestic water. In bithermic systems, the principle of separating the service areas of different environments also applies, but this applies specifically to the internal delimitation of the chambers. While the standard split heat exchanger initially contains two different chambers.
Structural device

Now it's time to deal with structural features bithermic radiators, which allow it to separately heat different media. Specialists characterize such structures with the concept of "pipe in pipe" or "section in section". If a conventional heat exchanger assumes a set of pipes that have a hollow niche, then the bithermic device is distinguished by internal division into several segments - these are zones in which water for hot water and heating circulates without mixing. And already according to the classical scheme, copper fins-plates are also attached to the pipes, which increase the heat transfer coefficient. Obviously, depending on the method of integration into the target equipment, other design features of the radiator will also be provided. In particular, the device of a bithermic heat exchanger of a gas boiler is oriented towards heating by a burner, so the body can provide additional layers of protection. It is mandatory for all heat exchangers to provide means of ensuring safety against short circuits of electric current. Since the circuits can be interfaced with other utility lines, grounding and the presence of fuses in the boiler stations are also mandatory.
How does a bithermic heat exchanger work?

Operating modes for heating and hot water supply have several differences. In the first case, standard heating of water occurs in the process of gas combustion - if we are talking about the same gas boilers, for example. That is, in the heating mode, the heat carrier is directly heated, which then circulates along its circuit. As for the operation mode in the DHW format, this function is somewhat secondary. The primary heating of the coolant also takes place, and already from it heat is transferred to sections with water intended for hot water supply. In this case, water for heating is not distributed through the corresponding circuits - it remains in its section. Almost all bithermic boilers have one rule - only one of the two circuits can work at the same time. Simultaneous circulation of water for heating and hot water is not allowed.
Boilers on bithermic heat exchangers
The use of bithermic radiators in boiler plants is becoming more widespread. Often major manufacturers they themselves develop model projects using their own components, including heat exchangers. One of the leaders in the segment is Immergas, which offers boilers with 6-tube heat exchangers. This design is a plus compared to 4 and 5 tube heat exchangers because the extended section can be located close to the burner flame. However, it is necessary to take into account the thermal power that the boiler will provide. The bithermic principle of operation in this case is capable of delivering about 24 kW, and this may be excessive for private houses and large country cottages. The companies Vaillant, Navien, Protherm are also developing bithermic units. The products of these manufacturers are distinguished not only by modern design, but also by functionality. Engineers strive to provide models with the ability to smoothly adjust the flame, the option of cooling the heat exchanger, etc.

Advantages of bithermic aggregates
The advantages of single block heat exchangers extend both to the efficiency of heating as such and to the convenience of control, not to mention the higher reliability of the units. As for efficiency, bithermic radiators operate with a lower heat loss coefficient. If a system divided into two blocks requires heating of two blocks, then in this case the filling of one body is serviced - accordingly, the amount of heat generated increases. In terms of control, a bithermic heat exchanger is more profitable for the same reason. Thermostats are guided by the indicators of one solid block, which affects the accuracy of the data obtained. Reliability, in turn, is achieved by minimizing the connecting infrastructure - in fact, only a connection is required between the heat exchanger and the supply channels.
Design flaws

The main disadvantage of the bithermic design is the limitation when working with liquids saturated with salts. In this context, one can note the imperfection of the monoblock case and the coaxial circuits inside, which are quickly covered with scale. In addition, a bithermic heat exchanger is not able to provide the same performance as in the case of split radiators. This applies specifically to hot water supply, since the design itself implies a smaller volume of water serviced for such tasks.
2013-01-23 10 529
In many European gas boilers, a bithermic heat exchanger is installed. Judging by the assurances of manufacturers, this reduces the cost of production and practically does not affect the heat transfer and efficiency of heating equipment.
On the Internet, on the contrary, you can find many articles warning against buying boilers with a bithermic heat exchanger. To figure out where the truth is, you need to learn about the design features and operation of the device.
How does a bithermic type heat exchanger work?
Bithermic heat exchanger in section, consists of two tubes of different diameters, made of heat-conducting material. The inner cavity is curved in the form of a rhombus. The main tube is made of copper, the inner tube is made of aluminum (metal may vary) depending on the manufacturer. From above by pressing or soldering, heat-accumulating plates are fixed.The principle of operation of a boiler with a bithermic type heat exchanger is as follows:
- The plates accumulate heat and heat the tubes with the coolant circulating in them. The first circuit, the main pipe of the heat exchanger, is designed for pumping liquid for the heating system, the second (in the form of a rhombus), for hot water.
- The boiler operation algorithm is as follows - until the hot water tap is opened, only the heat carrier of the heating system circulates through the heat exchanger. As soon as DHW is required, heating for heating is temporarily stopped.
It turns out that double-circuit gas boilers with a bithermic design of the heat exchanger operate on the principle of alternately heating the heating system and hot water, which allows more accurate use of the heat received from the burner.
The service life of the heat exchanger depends on several factors: chemical composition water for hot water supply, wall thickness laid down by the manufacturer. Weak point and at the same time, a disadvantage of bithermic heat exchangers is the susceptibility to sedimentation of scale inside the walls of the heat exchanger.
The heat generator with two separate heat exchangers will continue to work to heat the coolant after the DHW circuit is overgrown. The device of a bithermic heat exchanger of a gas boiler does not provide such an opportunity. After the overgrowing of the circuit, the operation of the boiler stops completely.
How and how to flush a heat exchanger with a bithermic design
Flushing the heat exchanger in bithermic boilers is mandatory and is prescribed in the operating instructions. In fact, the manufacturer has the right to refuse warranty service if this condition is violated. With timely flushing, a complete restoration of the heat exchanger is achieved - the capacity of the circuit.There are several ways to flush:
- At home, the simplest method is to fill the boiler with flushing liquid and pass it through the circuit, using a booster pump that creates pressure. The procedure takes 15-20 minutes and does not require dismantling the boiler.
The disadvantage of do-it-yourself repair is that some of the tools used are aggressive and improper performance of the procedure often leads to loss of tightness of the heat exchanger. Eliminating a leak between the circuits is quite problematic. A malfunction leads to the need to replace the heat exchanger. - IN service center – best option maintenance, allowing to extend the life of the boiler and prevent its early failure. Aggressive chemicals are used during service only if it was not possible to restore throughput by softer methods.
There are several more recipes for flushing the heat exchanger: using acetic or citric acid, etc. Folk ways are ineffective and do not bring significant benefits.
Which heat exchanger is better - separate or bithermic
The difference between a bithermic and a split heat exchanger lies not only in the principle of operation used. The diameter of the inner cavity of the contours differs.Two heat exchangers, working on hot water supply and separately for heating, are larger in diameter, therefore they grow longer and are less prone to calcium deposition on the walls.
When choosing between a separate heat exchanger or a bithermic one, one more factor is taken into account. The cost of the latest device is much lower. On average, the price per boiler is reduced by about a third. Low cost is the main advantage of the bithermic type heat exchanger.
If the heat exchanger is regularly cleaned, and a filtration and water treatment system is installed to feed the heating system and water supply, the bithermic boiler will last no less than an analogue with two separate circuits.


